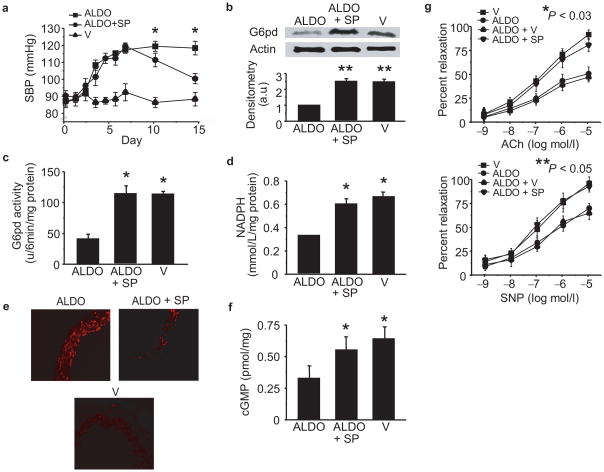
Figure 6. Spironolactone increases G6pd to improve vascular reactivity.
C3H wild-type mice were infused with aldosterone (50 μg/kg/day) (ALDO) (n = 20) or vehicle (V) (n = 20) via Alzet minipump for 14 d in the absence or presence of spironolactone (20 mg/kg/d) (ALDO + SP) (n = 20) added in the drinking water for the final 7 d of the 14 d treatment period, and (a) systolic blood pressure was measured by tail cuff (*P < 0.01 vs. ALDO). After the 14 d treatment period, aortas were harvested and (b) G6pd expression, (c) activity, and (d) Nadph levels were measured in tissue homogenates (*P < 0.01 vs. ALDO, n = 10). (e) Reactive oxygen species were examined in aorta sections by dihydroethidine fluorescence (200X magnification), and (f) cGMP levels were measured as an indicator of bioactive NO• (*P < 0.01 vs. ALDO, n = 6). Vascular reactivity was assessed by intravital videomicroscopy to increasing concentrations of (g) acetylcholine (Ach) (*P < 0.03 by ANOVA, n = 8) or sodium nitroprusside (SNP) (**P < 0.05 by ANOVA, n = 8). Densitometry was performed on a minimum of three blots and reported as arbitrary units (a.u.). Data represent mean ± SEM.