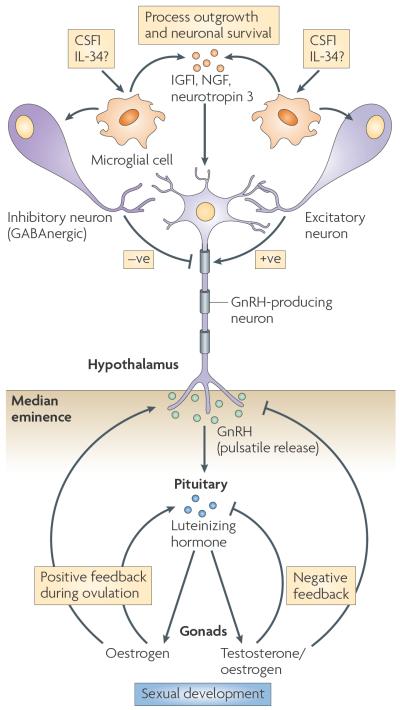
Figure 4. The trophic role of macrophages in neuronal patterning.
Microglial cells are a specialized type of macrophage found in the brain. These cells respond to colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor (CSF1R) signalling to produce factors that are required for the establishment of neuronal connectivity. Depletion of CSF1 shows that, among other things, microglial cells regulate the hypothalamic–pituitary–gonadal axis through negative signalling from neurons that respond to γ-aminobutyric acid A (GABAA neurons; known as GABAnergic) and positive signalling from excitatory neurons, which allows gonadotrophin-releasing hormone (GnRH) to be released in a pulsatile manner into the median eminence. This induces the release of luteinizing hormone by the pituitary, which controls testosterone and oestrogen biosynthesis in the gonads. IGF1, insulin-like growth factor 1; IL-34, interleukin-34; NGF, nerve growth factor.