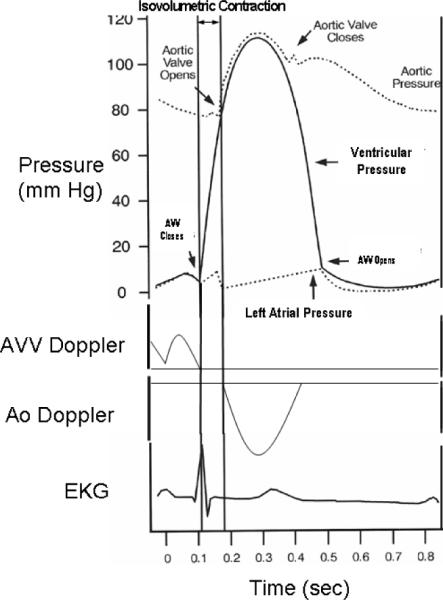
Top panel depicts a hypothetical ventricular, aortic and left atrial pressure tracing; next panels depict AV valve and aortic valve pulse-Doppler tracings, and bottom panel depicts EKG tracing. The peak pressure change during ventricular contraction (peak dP/dt) almost always occurs during isovolumetric contraction (IC). However, the ventricular pressure rise during IC is almost linear. Hence, Peak dP/dt ≈ Mean dP/dt
(Aortic diastolic pressure – ventricular end-diastolic pressure)/(IC time).
The IC time is calculated by subtracting the time interval between the onset of the QRS complex and the closure of the systemic AV valve (on AV valve inflow pulse Doppler tracing) from the time interval between the onset of the QRS complex and the opening of the aortic valve (on the aortic pulsed Doppler tracing). Aortic diastolic pressure is measured with a blood pressure cuff. Ventricular end-diastolic pressure is assumed to equal 5 mmHg. Because ventricular end-diastolic pressure is usually much less than aortic diastolic pressure, large errors in the estimation of ventricular end-diastolic pressure introduce relatively small errors into the calculation of mean dP/dt
.