Figure 2.
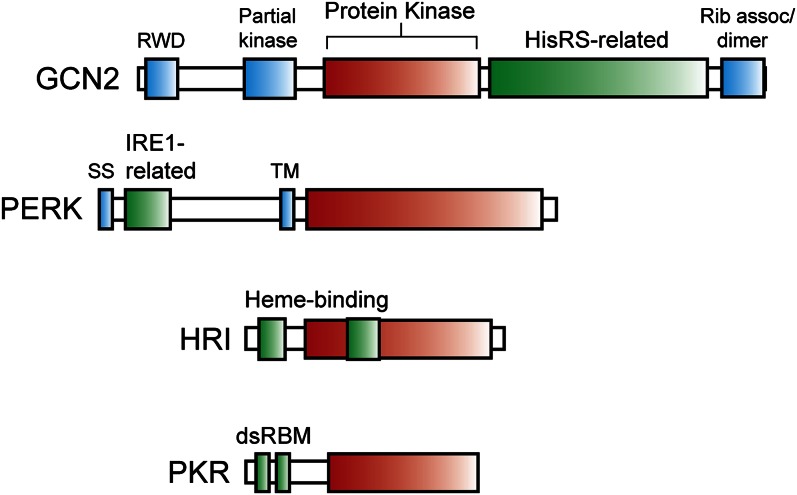
A family of eukaryotic initiation factor (eIF) 2α kinases are activated in response to diverse stress conditions. The eIF2α kinases possess a related protein kinase domain (red box) that is flanked by distinct regulatory sequences, which facilitate induction of phosphorylation of the α subunit of eukaryotic initiation factor 2 (eIF2α~P) in response to different stress conditions. Due to differences in the length of the characteristic insert sequences shared among eukaryotic initiation fact (eIF) 2α kinases, the size of the protein kinase domain differs among family members. The eIF2α kinase general control nonderepressible (GCN) 2 contains a RWD sequence that associates with the activator protein GCN1, a partial kinase domain required for GCN2 activation, histidyl-tRNA synthetase–related sequences (HisRS) that directly bind uncharged tRNA, which accumulate during nutritional stress, and a carboxy terminal region that facilitates GCN2 dimerization and its ribosome association. Note many of the functional features of these domains are based on studies for yeast GCN2, which shares the same domain arrangement (6). PKR-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase (PERK) contains an endoplasmic reticulum (ER) transmembrane segment (TM) that divides this eukaryotic initiation factor (eIF) 2α kinase in 2. The carboxy terminal protein kinase domain catalyzes eIF2α~P. The amino terminal portion features a signal sequence (SS), facilitating translocation of this portion of PERK into the lumen of the ER, and sequences related to the unfolded protein response sensor IRE1, which are suggested to monitor accumulation of unfolded protein in this organelle. HRI contains 2 regions that bind to heme, 1 at the amino-terminal portion of HRI and the second in the insert region of the protein kinase domain, which can repress this eIF2α kinase (29). Low levels of iron lead to reduced amounts of heme in erythroid cells, which triggers a release from this repressing mechanism and enhanced eIF2α~P. As a consequence, the availability of heme is tightly coupled to globin synthesis, the predominant translation product in erythroid tissues. PKR participates in an antiviral defense mechanism triggered by interferon. Two double-stranded RNA binding motifs (dsRBM) associate with double-stranded RNA that can accumulate in cells infected by viruses, leading to PKR autophosphorylation and enhanced eIF2α~P (30). Lowered protein synthesis would reduce viral replication and proliferation. HisRS, histidyl-tRNA synthetase; Rib assoc, ribosome association; TM, transmembrane.