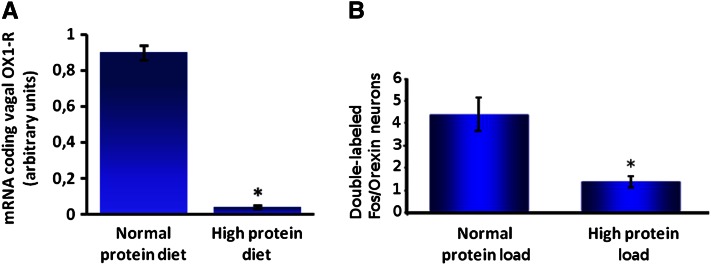
Figure 3.
A high-protein load (55% protein as energy) compared with a normal protein (NP) load (14% protein as energy) leads to decreased messenger RNA expression of orexin-1 receptor in nodose ganglia (A) and decreased activity of orexin neurons in the lateral hypothalamus (B). A, Effect of a high-protein (HP) diet on messenger RNA expression of orexin-1 receptor (OX1-R) in nodose ganglia. Male mice were adapted for 15 d to their respective diets: NP or HP diet (n = 6). Mice were fasted overnight and killed 2 h after receiving an intragastric load of their respective diets (4.07 kcal). To measure orexin-1 receptor expression, 4 nodose ganglia were pooled in each observation. Primers used in this experiment (5′-3′) are OX1-R sense (ACGGCGAGCTGTGCTCTT), OX1-R antisense (CCTGGACCGCTGGTATGC), 18S-sense (ACGGAAGGGCACCACCAGGAG), and 18S antisense (GACCCACCACCCACGGAAACG). Results represent relative expression compared with 18S (2−ΔCT; CT = CTORX1-R − CT18S) ± SEM. *Significant effect of diet (P ≤ 0.05). Adapted from Reference 55 with permission. B, Effect of an intragastric load of protein on the activity of orexin neurons in the LH in rats. Male rats (n = 18) adapted to an NP diet were separated into 2 groups (n = 9), fasted overnight, and killed 90 min after receiving an intragastric load (10.5 kcal) of an NP or HP diet. Rats were perfused intracardially with saline and 4% paraformaldehyde in PBS, and brains were then cryoprotected in 30% sucrose. Transverse 20-μm thick lateral hypothalamus sections were cut with a cryostat (Bregma −3,70; −1,30). Briefly, sections were mounted on slides, dried overnight, and frozen (−20°C). For immunochemistry, slides were rinsed in PBS, incubated in 2% bovine serum albumin for 60 min, incubated for 24 h with rabbit anti–c-Fos antibody (1:1000) (Calbiochem) at room temperature. Sections were then placed for 3 h at room temperature with a biotyinlated goat anti-rabbit secondary antibody (1:200) diluted in PBS-bovine serum albumin, and revealed with diaminobenzidine (Sigma). c-Fos staining was followed by neuronal phenotype staining [primary antibody rabbit anti-orexin (Oncogene), 1/100; anti-rabbit secondary antibody, 1:200 (Vector)]. Orexin neurons were revealed by reaction with an Elite Vectastain SG kit (Vector). After washing and drying overnight, sections were cleared in ethanol and xylene. Results are presented as means ± SEM per section. *Significant effect of the load P ≤ 0.01. Adapted from Reference 65 with permission.