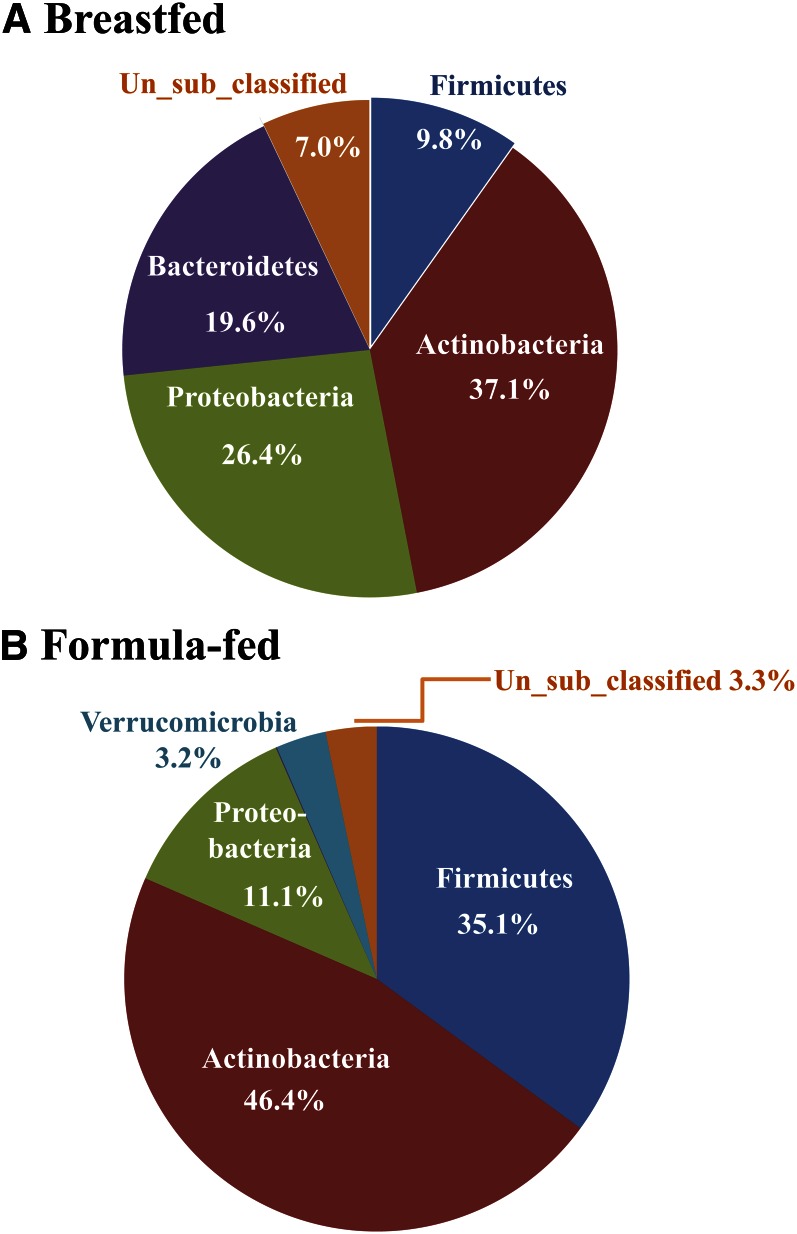
Figure 3.
Bacterial phyla in stool of 3-mo-old breast- and formula-fed infants. Genomic DNA was extracted from stool and the bacterial 16S recombinant RNA gene V1 to V3 regions were amplified with primers 27F RegS and 534R. Primer 27F RegS contained sequencing primer and barcode (MID). PCR products were purified and quantified, and amplicons were mixed in equimolar concentration and sequenced using 454 Life Sciences Genome Sequencer FLX with GS FLX Titanium series reagents at the Keck Center for Comparative and Functional Genomics at the University of Illinois, Urbana. 16S recombinant RNA gene sequences were processed and analyzed using the Mothur program (63). Sequences were classified to phylum by comparing with RDP training set. Breast-fed infants had a higher percentage of Bacterodetes and lower Firmicutes and Verrucomicrobia compared with formula-fed infants.