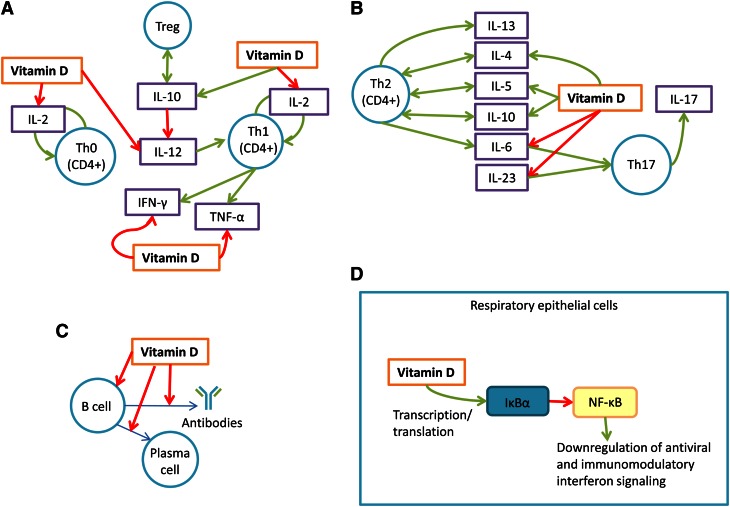
Figure 1.
Vitamin D and its various actions in the immune system. (A) Vitamin D inhibits the production and proliferation of Th1 and Th0 cells by inhibiting IL-2, IFNγ, and TNFα vitamin D promotes the production of Treg cells by facilitating production of IL-10. (B) Vitamin D promotes a Th2-mediated immune response profile by promoting IL-4, IL-5, and IL-10. Vitamin D inhibits a Th17-mediated immune response profile (and thus inhibits IL-17) by inhibiting IL-6 and IL-23. (C) Vitamin D inhibits the production of B-cells, the differentiation of B-cells into plasma cells, and the production of antibodies by B-cells. (D) Vitamin D promotes nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells inhibitor, α in respiratory epithelial cells, which inhibits NF-κB, in turn promoting antiviral and immunomodulatory interferon signaling. Th, T helper cell; Treg, T regulatory cell.