Figure 1.
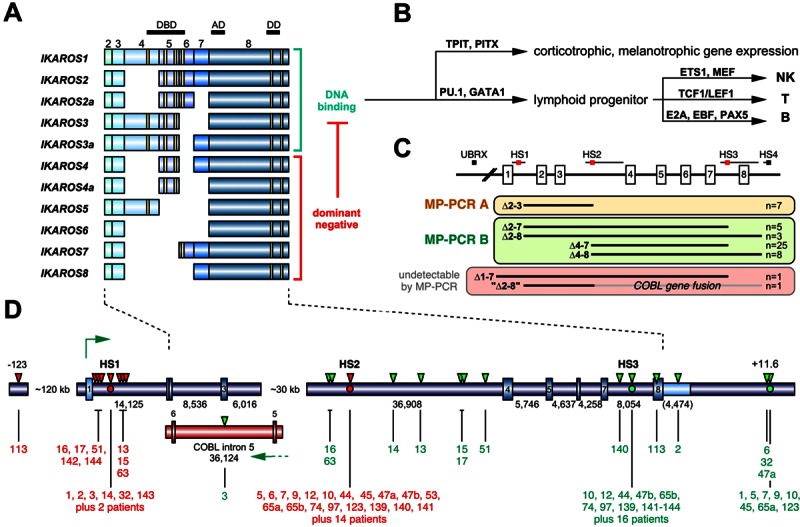
The human IKZF1 gene and its role in the biology. A. Summary of IKZF1 transcripts. IKZF1 is composed of 8 exons, of which the first one is noncoding. Several splice forms of IKZF1 transcripts have been described in the literature (n=11). Important functional domains are encoded by exon 4-6 (4 zinc fingers) and exon 8 (2 zinc fingers). At least 3 N-terminal zinc fingers are necessary for DNA binding. Therefore, 6 out of 11 IKZF1 splice variants are described to encode dominant-negative versions of IKAROS, because they are still able to dimerize with bona fide protein variants via the C-terminal zinc finger domains. B. The complex biology behind IKAROS protein variants is necessary to (a) regulate hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis. IKAROS steers with TPIT and PITX transcription factors the corticotrophic and melanotrophic gene expression; (b) control hematopoietic development. IKAROS determines the devlopment of NK, T and B cells in concert with PU.1, GATA factors and the other depicted transcription factors. C. Overview of the results of the MLPA analysis of the 48 identified IKZF1-deleted BCP-ALL patients (that exhibited 50 breakpoints). All deletions within the IKZF1 gene can be clustered into 4 different groups (indicated by the 3 colored panels and a fourth group of leukemia patients that lost their complete IKZF1 allele). Four different recombination hotspots (HS1-4) and a single upstream breakpoint (UBRX) were identified. Two of these 4 patient classes can be readily analyzed by the established multiplex PCR reactions A and B, respectively. The third group can only be investigated by LDI-PCR analyses. The fourth group can only be detected by MLPA analyses. D. The gene structure of human IKZF1 is shown. Exons are depicted as rectangles. Below: Sizes of the individual introns and the 3-NTR (in brackets). There is a gap of about 30 kb for which no sequence data are available from public databases. Thus intron 3 must be divided in intron 3a (6,016 bp) and intron 3b (36,908 bp), separated by a gap (hampering our LDI-PCR analyses because no oligonucleotides can be designed). Published fusion sites between HS1 and HS3 or HS2 and HS3 are indicated by red or green dots. All fusion sites identified in this study are indicated by red (5’-breakpoint) and green (3’-breakpoint) triangles above the gene structure and by black lines below the gene structure. Each breakpoint could be assigned to a patient by its UPN. In addition, a small portion of the COBL gene is shown. The tail-to-tail gene fusion between IKZF1 intron 1 and COBL intron 5 is due to an interstitial deletion of about 800,000 kb between 7p12 and 7p12.1. The novel HS4 breakpoint is located about 11.6 kb downstream of the IKZF1 gene. Patients identified by the published direct genomic PCR approach are indicated as non-numbered “patients” (n=16).
