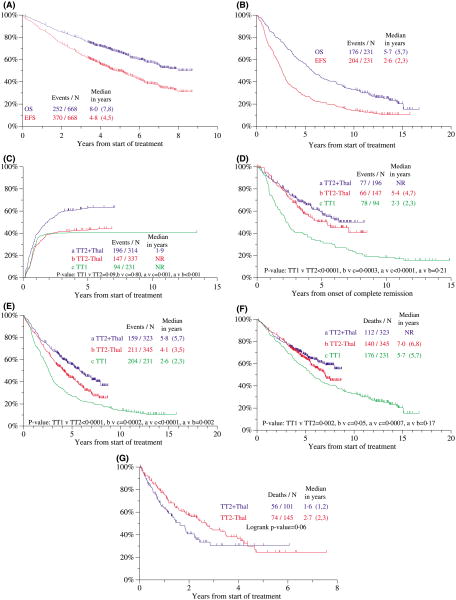
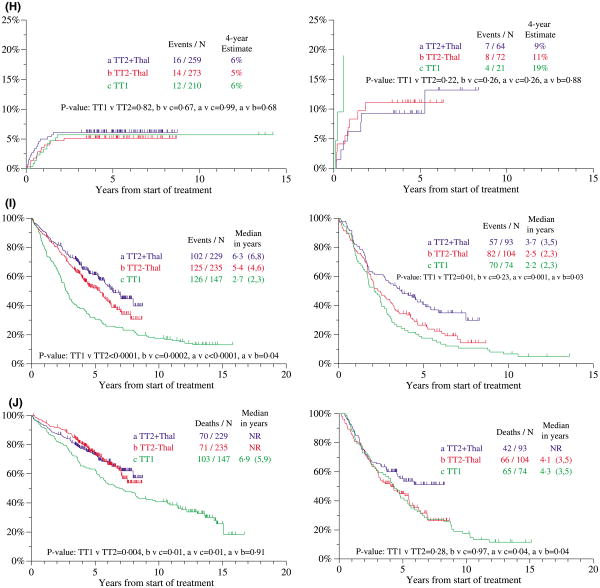
Fig 3.
Kaplan–Meier plots of clinical outcomes with total therapy 2 (TT2) and total therapy 1 (TT1). (A) The median durations of overall survival (OS) and event-free survival (EFS) for all 668 patients enrolled in TT2 were 8.0 and 4.8 years respectively. (B) The median durations of OS and EFS for all 231 patients enrolled in TT1 were 5.7 and 2.6 years respectively. (C) Cumulative proportions of patients achieving complete remission (CR) counted from initiation of TT1 and TT2. Patients randomized to the thalidomide arm of TT2 (TT2 + THAL) had a significantly higher CR rate than those on the control arm of TT2 (TT2 − THAL), while there was no difference between CR rates achieved with TT1 and TT2−THAL. NR, not reached. (D) Duration of CR from onset of CR. Patients enrolled in TT2 had superior CR durations versus those treated on TT1; no difference was noted between the two arms of TT2. NR, not reached. (E) EFS of patient's enrolled in TT2 and TT1 from initiation of therapy. EFS was superior with TT2 + THAL versus TT2 − THAL, and both arms of TT2 were superior to TT1. (F) OS of patient's enrolled in TT2 and TT1 from initiation of therapy. OS was superior among patients treated with TT2 (both arms) compared to those treated with TT1, while TT2 + THAL was not superior to TT2 − THAL. Note a separation of survival curves between the two arms of TT2 emerging at 5 years. NR, not reached. (G) Postrelapse survival by treatment arm of TT2. Patients randomized initially to thalidomide (THAL) tended to fare better than those on the control arm (No THAL). (H) Treatment-related mortality with TT2 and TT1 according to age (<65 years, left; ≥65 years, right). Similar outcomes were observed in the younger age group regardless of treatment; as a group, the older age cohort experienced higher treatment-related mortality than their younger counterparts (P = 0.002). (I) EFS of patients treated with TT2 and TT1, according to the presence of cytogenetic abnormalities (CA). Overall, patients enrolled in TT2 fared better than those enrolled in TT1, regardless of CA status. Among patients without CA, both TT2 arms were individually superior to TT1, and TT2 + THAL was superior to TT2 − THAL. In the cohort with CA, patients treated with TT2 + THAL fared better than patients on TT2 − THAL, which was not superior to TT1. (J) Overall survival (OS) of patients treated with TT2 and TT1, according to the presence of CA. Overall, patients without CA fared better when enrolled in TT2 than those enrolled in TT1, while there was no difference between the two arms of TT2. Among patients with CA, those on the TT2 + THAL arm fared better than either TT1 or TT2 − THAL groups. NR, not reached.