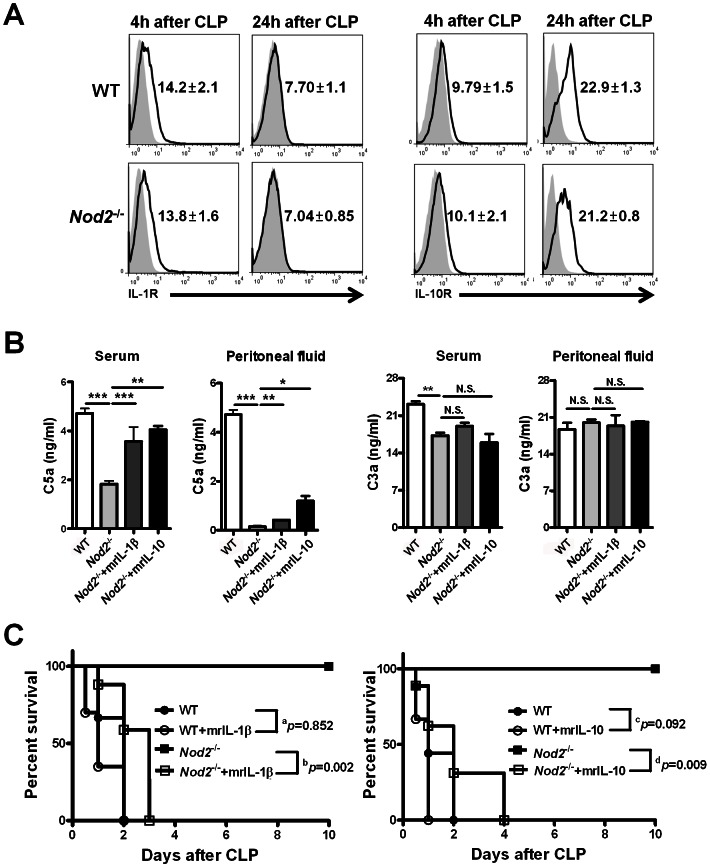
Figure 3. IL-1β-dependent IL-10 production mediated by nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain (NOD) 2 enhances C5a generation during cecal ligation and puncture (CLP)-induced sepsis.
(A) IL-1 and IL-10 receptor expression was estimated on total peritoneal cells in terms of mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) from WT (n = 3) and Nod2−/− (n = 3) mice 4 h and 24 h after CLP. (B) Serum and peritoneal C5a and C3a levels were measured 24 h after CLP in WT (n = 4) and Nod2−/− (n = 4) mice injected with recombinant IL-1β or IL-10 prior to CLP. (C) The survival percentages of WT and Nod2−/−mice injected with recombinant IL-1β or IL-10 were measured during CLP-induced sepsis (aP = 0.852 [not significant], bP = 0.002, cP = 0.092 [not significant],dP = 0.009, log-rank test; WT [n = 11], WT mice injected with recombinant IL-1β [n = 6] or IL-10 [n = 6], Nod2−/− [n = 10], and Nod2−/− mice injected with recombinant IL-1β [n = 8] or IL-10 [n = 8]). *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 (one-way ANOVA [b]). Results shown are representative of three independent experiments except for (C) (mean and SEM).