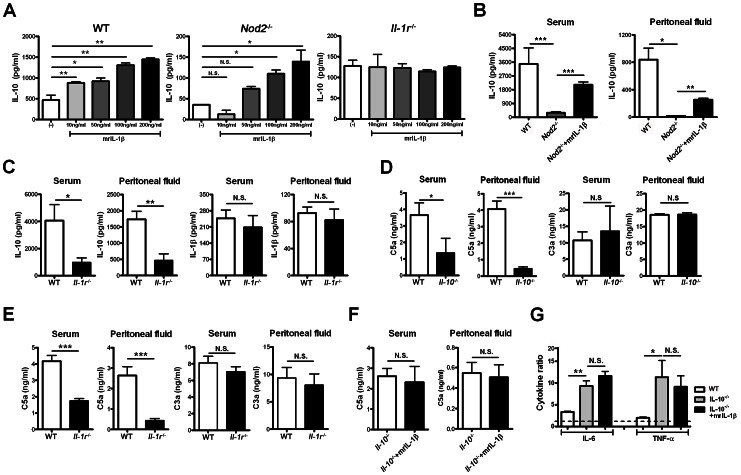
Figure 4. Nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain (NOD)2-mediated IL-1β-dependent IL-10 production by neutrophils enhances C5a generation during sepsis.
(A) Peritoneal cells obtained from WT, Nod2−/−, or Il-1r−/− mice 12 h after CLP were incubated with recombinant IL-1β for 12 h and IL-10 levels were measured in culture fractions. (B) Serum and peritoneal IL-10 levels were measured in WT, Nod2−/− and Nod2−/− mice injected with recombinant IL-1β 4 h after CLP. (C) Serum and peritoneal IL-10 and IL-1β levels were measured in WT and Il-1r−/− mice 24 h after CLP. (D–F) Serum and peritoneal C5a and C3a levels were measured in WT, Il-10−/− (D), Il-1r−/−(E), and Il-10−/− mice injected with recombinant IL-1β 4 h after CLP (F). (G) Recombinant IL-1β was injected into Il-10−/− mice 4 h after CLP. Peritoneal cells obtained from these mice were incubated with or without LPS and cytokine levels were measured. The ratios of individual cytokines (stimulated with LPS/non-stimulated) were estimated. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 (one-way ANOVA [a, b, g]), two-tailed unpaired t-test [c–f]) (n = 4 in B–G) Results shown are representative of three independent experiments (mean and SEM).