Figure 6. Infectivity and particle budding of Gag mutants.
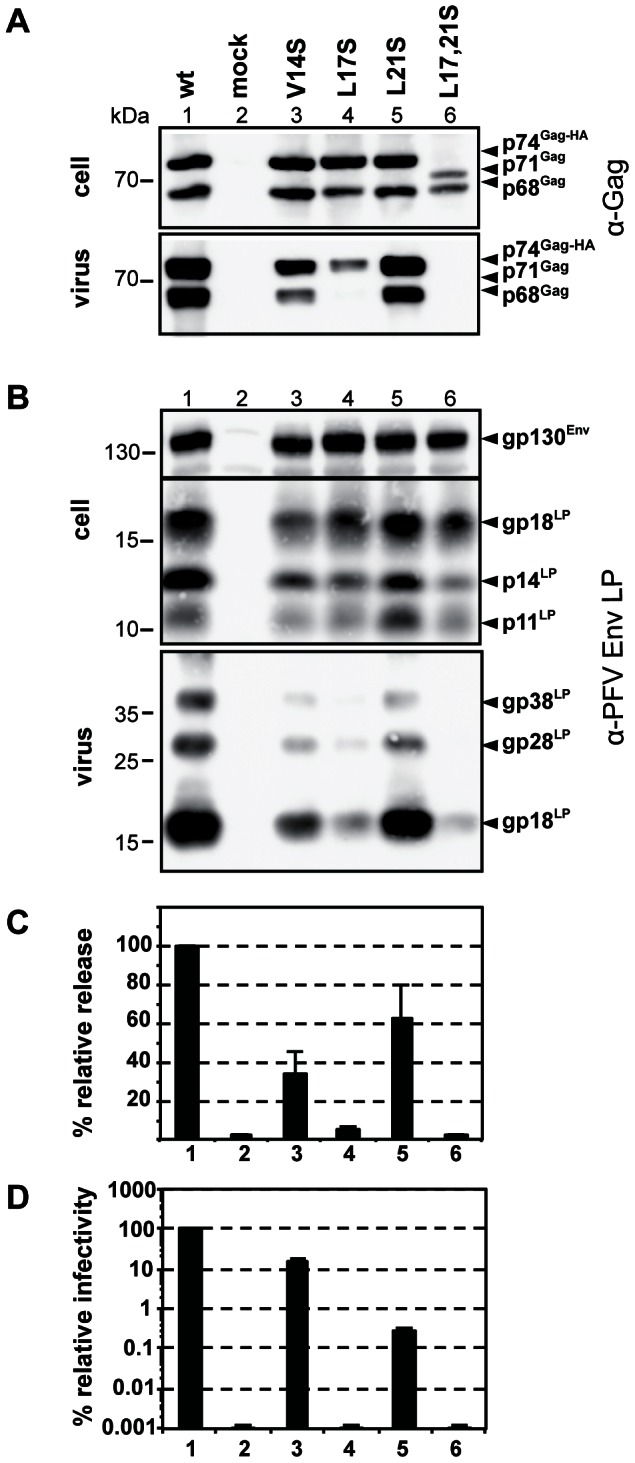
293T cells were co-transfected with equal amounts of PFV transfer vector puc2MD9, Env packaging construct pcoPE, Pol packaging construct pcoPP and various Gag packaging constructs (wt: pcziPG CLHH; V14S: pcziPG CLHH V14S; L17S: pcziPG CLHH L17S; L21S: pcziPG CLHH L21S; L17, 21S: pcziGag4 L17, 21S) or only with pUC19 (mock) as indicated. Western blot analysis of cell lysates (cell) and pelleted viral supernatants (virus) using (A) polyclonal antibodies specific for PFV-Gag (α-Gag) or (B) rabbit polyclonal antibodies specific for PFV Env-LP (α-LP). The identity of the individual proteins is indicated on the right. (C) Relative amounts of released Gag and RT quantified from Western blots from two independent experiments (n = 2–4). (D) Relative infectivity of extracellular 293T cell culture supernatants using an eGFP marker gene transfer assay were determined 3 days post infection. The values obtained using the wild type Gag packaging vector were arbitrarily set to 100%. Absolute titres of these plain supernatants were 8.7±3.3×106 EGFP ffu/ml. Means and standard deviations of three independent experiments (n = 3–6) are shown.
