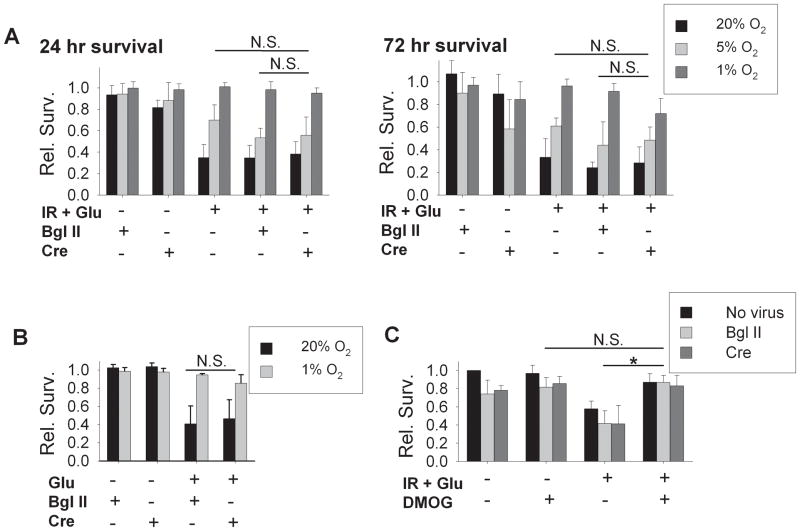
Figure 8. The role of HIF-1α in hypoxia-induced protection against delayed ischemia-reperfusion injury.
All data are from neurons cultured from HIF-1α fl/fl mice, treated at day 1 with 100 M.O.I. empty viral vector Bgl II or with AdV cre-GFP, as indicated. A) Delayed relative survival at 24 hours and 72 hours following simulated ischemia-reperfusion (with glutamate) in neurons cultured for 10 days in 20% O2, 5% O2, or 1% O2 conditions. HIF-1α knockout, in cre-exposed neurons, did not prevent the hypoxia-induced protection (n = 5; N.S., groups not significantly different by two-way ANOVA). B) Excitotoxic injury assayed 24 hours after 60 min exposure to 100 μM glutamate. HIF-1α knockdown with AdV cre-GFP produced no loss of protection against excitotoxic death in neurons from 1% O2 (relative survival, n = 4; cre group compared to Bgl II group not significantly different by two-way ANOVA; effects of O2 level remained significant). C) Effect of prolyl hydroxylase inhibition. Relative survival 24 hours after simulated ischemia-reperfusion in neurons from 20% O2 conditions treated with DMOG (25 μM). Significant protective effects of DMOG were not affected by HIF-1α knockdown in cre-exposed neurons (n = 4; cre group compared to Bgl II group not significantly different by two-way ANOVA; *significant protection by DMOG, p<0.001).