Figure 1.
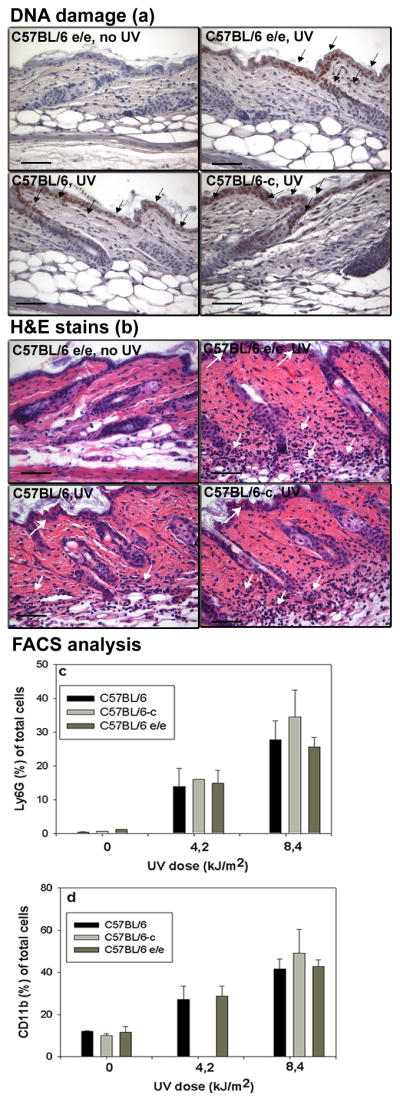
(a) DNA damage in mouse skin within 1h after irradiation with 8.4 kJ/m2 UV irradiation detected by antithymine dimer antibody conjugated with HRP. DNA damage (brown nuclear staining marked by black arrows). Bar= 50μm.
(b) H&E stain of adult mouse skin 48h after UV irradiation (8.4 kJ/m2). White arrows designated infiltrating inflammatory cells. Bar= 50μm.
Dose dependent infiltrate of Ly6G+ cells (c) and CD11b+ cells (d) in adult C57BL/6-c (albino), C57BL/6-Mc1re/e (yellow) and C57BL/6 (black) mouse skin 48h after UV irradiation. Significant difference between UV irradiated and untreated skin (t-test, p <0.001) in each group. No differences between the UV response in the 3 tested groups of mice (p=NS, ANOVA).
