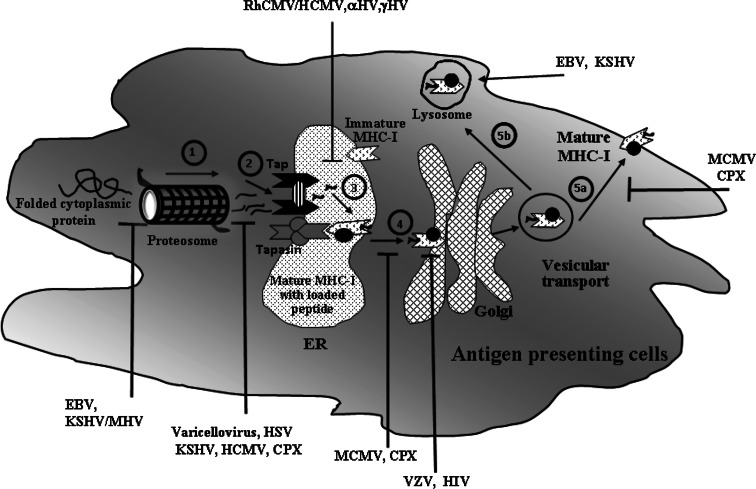
Fig. 1.
Immune regulation through inhibition of MHC class I associated antigen presentation pathway during viral infection. An outline of virus mediated inhibition of various stages of MHC class-I antigen presentation pathways for recognition of CD8+ T cell has been described in this figure along with few examples of viruses that inhibit the specific step to escape immune evasion strategies. 1 The degradation of viral proteins by proteasome to generate small peptides. Epstein Barr virus (EBV), Kaposi’s sarcoma associated virus (KSHV) and Murine gamma herpes virus (MHV) escape the proteasomal degradation of viral proteins into antigenic peptides with the help of different viral proteins [27, 38, 77, 147]. 2 Translocation of proteasome generated peptides into the ER to bind TAP. Different proteins of Varicellovirus, Kaposi’s sarcoma associated virus (KSHV), Herpes Simplex virus (HSV), Cow Pox Virus (CPX) and Human Cytomegalovirus (HCMV) act as inhibitors of TAP, block the peptide and ATP binding and thereby inhibit TAP-mediated peptide transport [58, 90, 132]. 3 Formation of mature MHC class I molecule from nascent MHC class I molecule by addition of TAP, β2 microglobulin, calreticulin, ERp57 and tapasin in ER. Rhesus CMV (RhCMV)/HCMV interferes with the function of tapasin. HCMV, alpha and gamma herpes viruses restrict MHC-I molecule in ER. Adenovirus also retains MHC-I molecules in ER [36, 45, 65, 106]. The complex assembly of the mature MHC complex has been simplified and depicted with a small circle, filled in black. 4 Translocation of peptide loaded mature MHC class I to Golgi. For example, Murine cytomegalovirus (MCMV) and CPX inhibit the transport of mature MHC-I molecules out of the ER membrane. HIV-1 protein, Nef diverts MHC-I trafficking from the trans-Golgi network to the lysosomal compartment [109, 145]. Varicella zoster virus (VZV) retains mature MHC-I complexes in the cis/medial Golgi of the trans-Golgi network that regulates the vesicular trafficking of these molecules [36]. 5a Transport of peptide loaded mature MHC from Golgi to cell surface for antigen presentation to CD8+ T cell. For example MCMV gp48 and CPX can restrict MHC-I transport from Golgi and redirect it to lysosome [19, 113]. 5b Degradation of peptide through lysosomal and/or autophagy pathway [24]. EBV and KSHV enhance the endocytosis and lysosomal degradation of mature MHC-I molecule of the cell surface [95, 151]