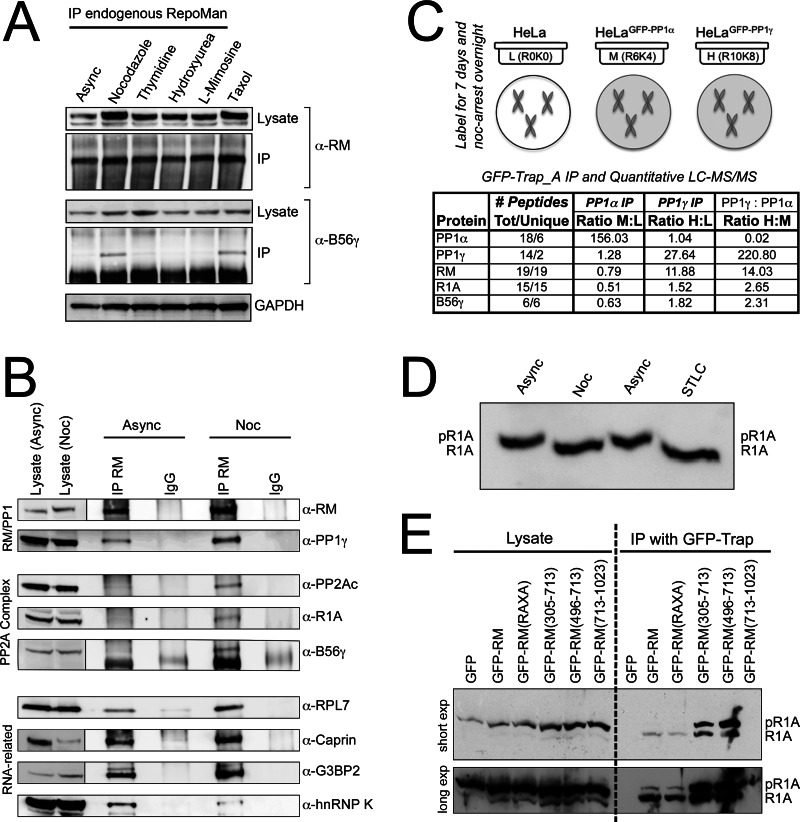
Fig. 5.
Mitosis-specific association of RepoMan/PP1 and PP2A/R1A/B56γ. A, IP/WB analysis demonstrating copurification of B56γ with endogenous RepoMan (RM) predominantly from extracts prepared from cells arrested in mitosis (using nocodazole or taxol), as compared with asynchronous cells or cells arrested in S-phase (using thymidine, hydroxyurea or l-mimosine). Lysate lanes demonstrating the relative amounts of RepoMan and B56γ (and the loading control GAPDH) before IP are shown below the IP lanes. B, IP/WB analysis of endogenous RepoMan immunoprecipitated from either asynchronous or nocodazole (noc)-arrested cell extracts, compared with an IgG control IP. The WB was probed with the antibodies indicated. C, Quantitative comparison of GFP-PP1α and GFP-PP1γ interactomes in nocodazole-arrested cells. Specific enrichment of RepoMan and PP2Ac/R1A/B56γ with the γ isoform is indicated by high H:L and H:M ratios and low M:L ratios. PP1α is shown for comparison (high M:L ratio, and low H:L and H:M ratios). D, Phos-tag gel/WB analysis of R1A in asynchronous cell extracts versus extracts from cells arrested in early mitosis (using nocodazole or the Eg5 inhibitor STLC). The Phos-tag amplifies phosphorylation-induced band shifts. E, Phos-tag gel/WB analysis of R1A copurified with FP-tagged wild type RepoMan, the RAXA mutant and the 305–713 and 713–1023 fragments. Control GFP alone and RepoMan/713-1023 IPs are shown for comparison.