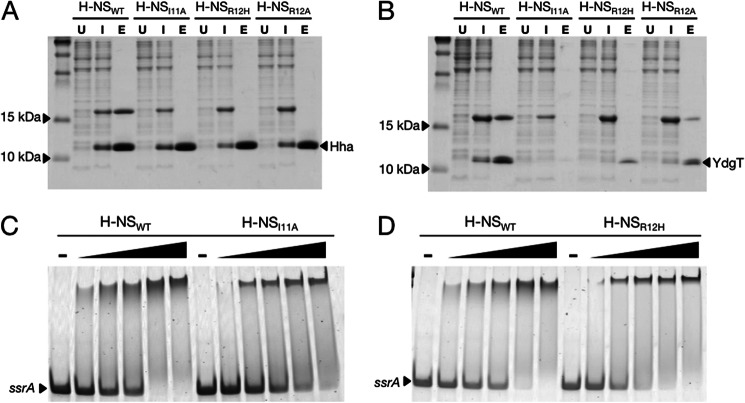
FIGURE 2.
H-NS mutations at residues Ile-11 and Arg-12 disrupt the Hha/H-NS and YdgT/H-NS interactions without affecting DNA binding activity in vitro. A, Coomassie-stained SDS-PAGE of His6-tagged Hha co-expressed with FLAG-tagged H-NSWT, H-NSI11A, H-NSR12H, and H-NSR12A. Samples from co-expression cultures were taken prior to induction with isopropyl 1-thio-β-d-galactopyranoside (lanes marked U (for “uninduced”)), 16 h after the addition of 1 mm isopropyl 1-thio-β-d-galactopyranoside (lanes marked I (for “induced”)), and after purification by nickel chromatography (lanes marked E (for “eluate”)). His6-tagged Hha copurifies with H-NSWT but not the point mutants H-NSI11A, H-NSR12H, and H-NSR12A. B, nickel resin purification of His6-tagged YdgT after co-expression with the same H-NS constructs in A. C and D, purified H-NSWT, H-NSI11A, and H-NSR12H were added to a 300-bp PCR fragment from the ssrA promoter region at concentrations of 150, 200, 300, 400, and 500 nm. The dash above four of the lanes indicates that no protein was added to the samples. Protein-DNA binding reactions were separated on a 6% polyacrylamide gel by native gel electrophoresis and stained using SYBR Green nucleic acid stain. The H-NS point mutants H-NSI11A and H-NSR12H shift the ssrA promoter fragment at similar concentrations as H-NSWT.