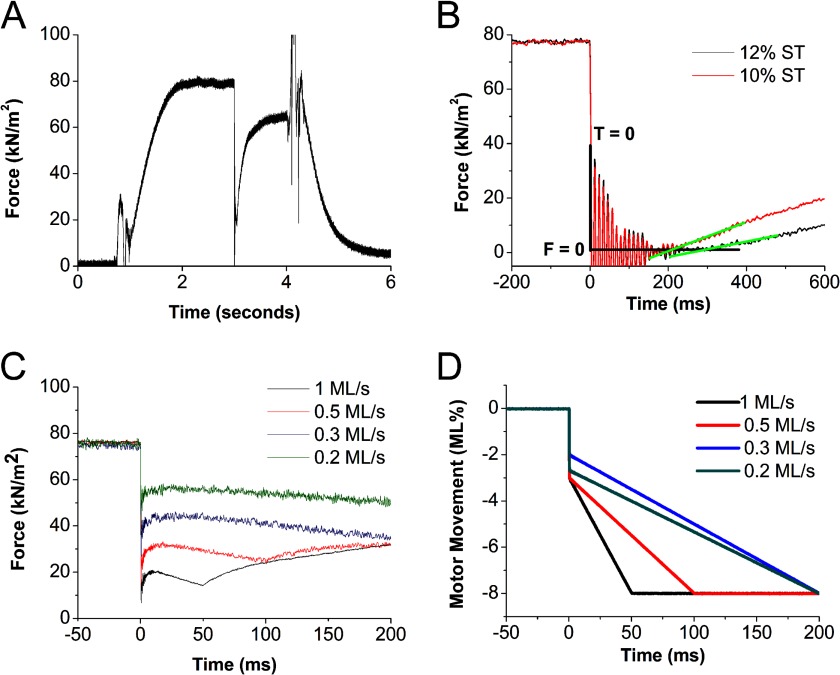
FIGURE 1.
A, representative tension trace during a temperature jump activation between 0.5 and 20 °C of a permeabilized trabeculum. Force rises to a isometric plateau. 3 s after the temperature jump, the muscle is rapidly released and shortened at a fixed velocity for 50 ms, and then force recovers at the shortened sarcomere length. Muscle is then restretched to the original length and relaxed in a low calcium solution at 4 s. B, tension traces during two slack test (ST) measurements encompassing a 10% rapid release (black trace) and 12% rapid release (red trace). Time zero (T = 0) is reset to mark the time of the onset of the release. The time taken for tension to deviate from zero “slack force” (F = 0) in each slack length test is used to calculate peak unloaded shortening velocity (Vmax). Shown are tension traces during a range of fixed velocities (C) and the corresponding motor traces showing the release lengths and ramp velocities of each maneuver (D). kN, kilonewtons. ML, muscle lengths.