FIGURE 4.
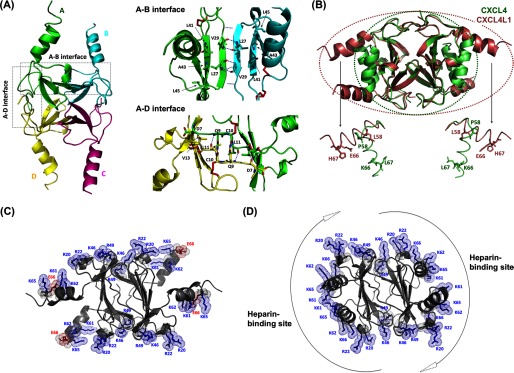
Crystal structure of CXCL4L1. A, shown is a schematic representation of CXCL4L1 tetramer (left) and the A-B and A-D interface where A/B/C/D monomer subunits are depicted by different colors. The hydrogen bonds for monomer association in A-B and A-D dimer interfaces are indicated by dotted lines. The residues constituting the exposed hydrophobic surface in A-B interface are shown as well as the residues responsible for association of N terminus in A-D interface. B, shown is the superposition of CXCL4 (PDB code 1F9Q) and CXCL4L1. The β-sheet core domain is almost identical, but helix α1 is rotated by ∼87° in CXCL4L1 relative to CXCL4, thus altering the overall shape of the molecule. The positions of the three mutations are indicated in two of the subunits by sticks. C, the distribution of positively charged residues and Glu-66 in CXCL4L1 is shown. D, the distribution of positively charged residues in CXCL4 is shown. The surrounding positive region is purposed to be able to recruit two individual anionic polysaccharides.
