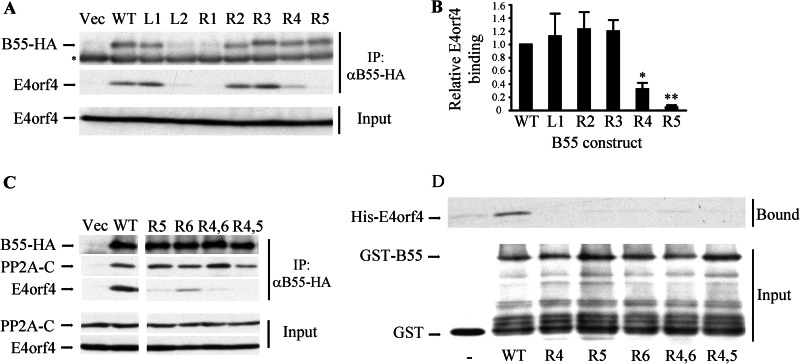
FIGURE 5.
B55α mutants bind E4orf4 at significantly reduced levels. A, clone 13 cells were transfected with an empty vector (Vec) or with plasmids expressing HA-tagged wild type B55α (WT) or various mutant B55α proteins. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with HA-specific antibodies, and immune complexes as well as input lysates were separated by SDS-PAGE and subjected to Western blot analysis with E4orf4- or PP2A-B55-specific antibodies. Input protein levels represent 10% of total protein amounts used for the immunoprecipitation (IP). The asterisk marks the endogenous PP2A-B55 band, which is detected similarly in all lanes, thus serving as a loading control. B, the levels of B55α and E4orf4 proteins in the immune complexes were quantified by densitometry, and E4orf4 binding levels were normalized to B55α expression levels. E4orf4 binding by WT B55α was defined as 1. Mutants L2 and R1, which were expressed at significantly reduced levels, were not subjected to the quantitative analysis. The graph summarizes the results of three independent experiments, and error bars represent S.E. A paired one-tailed t test indicated that E4orf4 binding to R4 and R5 was reduced significantly relative to its binding to WT B55α (*, p = 0.009 for R4; **, p = 0.0005 for R5), whereas there was no statistically significant difference between the binding of the other three well expressed mutants and the WT protein. C, experiments with additional B55α mutants were carried out as in A. Western blots were stained with antibodies to the HA tag, PP2A-C, and E4orf4. Double mutants were R4,6: R4+R6; R4,5: R4+R5. D, GST fused to the WT B55α subunit of PP2A or to B55α mutants as well as GST alone and His-E4orf4 were expressed in bacteria. The GST proteins were purified on glutathione beads and incubated with His-E4orf4. Bound E4orf4 and input GST proteins were detected by a Western blot.