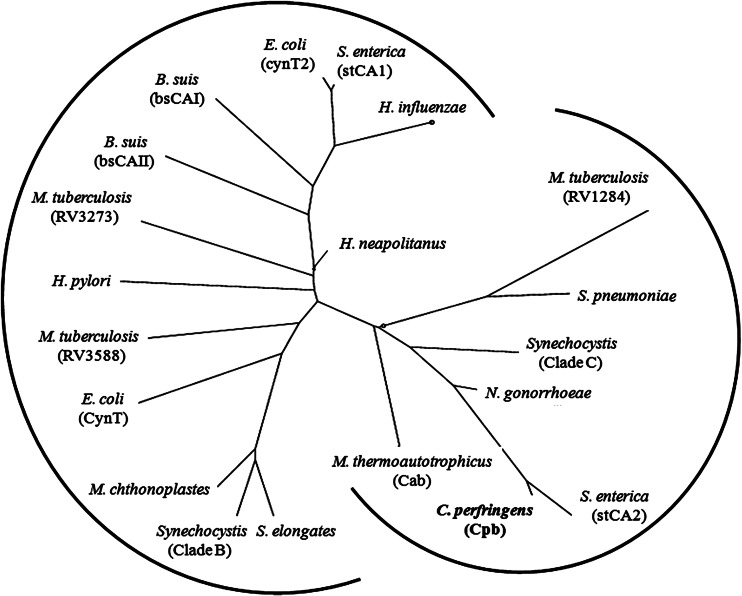
Fig 2.
Phylogenetic analysis of prokaryotic β class carbonic anhydrases. The sequences were from the following species (gene identification numbers shown in parentheses or brackets): Clostridium perfringens strain 13 (gi|18309395), Methanothermobacter thermautotrophicus strain ΔH (gi|15679577), Escherichia coli (cynT [gi|386607709] and cynT2 [gi|14277938]), Brucella suis (bsCAI [gi|260567947] and bsCAII [gi|260568899]), Helicobacter pylori (gi|188526816), Mycobacterium tuberculosis (strain RV1284 [gi|298524787], RV3588C [gi|15610724], and RV3273 [gi|15610409]), Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium (stCA2 [gi|378987335] and stCA1 [gi|16763561]), Neisseria gonorrhoeae (gi|59802380), Streptococcus pneumoniae (gi|307066706), Haemophilus influenzae (gi|99031788), Synechocystis (clade C [gi|1001130] and clade B [gi|1653251]), Synechococcus elongates (gi|56685078), Microcoleus chthonoplastes (gi|78057950), and Halothiobacillus neapolitanus (gi|88193005). The tree was constructed using the phylogeny/evolution analysis tools obtained at ExPASy (http://expasy.org/phylogeny_evolution). A distance-based method was used for the construction.