Fig 3.
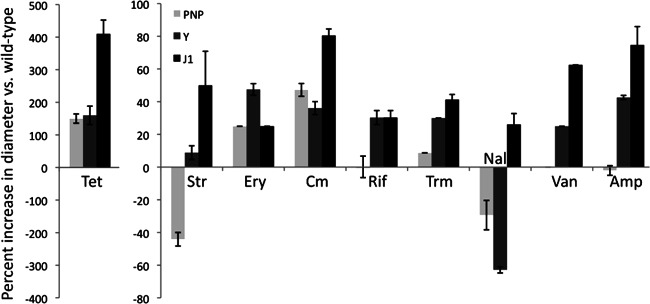
RNase Y and RNase J1 mutants are hypersensitive to antibiotics. Histograms show the percent increase in the diameter of the zone of inhibition compared to the wild type in filter disk assays (see the text). The PNPase mutant was included as a control. Disks (5 mm) were impregnated with 3 μl of antibiotic solutions at the following concentrations: tetracycline (Tet) at 2 mg/ml, streptomycin (Str) at 40 mg/ml, erythromycin (Ery) at 0.5 mg/ml, chloramphenicol (Cm) at 4 mg/ml, rifampin (Rif) at 4 mg/ml, trimethoprim (Trm) at 0.6 mg/ml, nalidixic acid (Nal) at 4 mg/ml, vancomycin (Van) at 2 mg/ml, and ampicillin (Amp) at 4 mg/ml. Values are the averages of data from 2 experiments with standard deviations as shown. Curiously, the zones of inhibition of the RNase mutant strains caused by tetracycline are significantly larger than those for other antibiotics, hence the different scale.
