Fig 1.
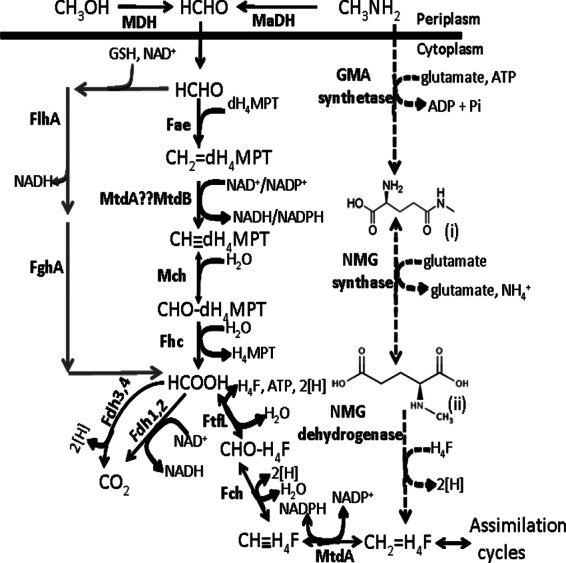
Methanol and methylamine oxidation pathway. Gene products involved in each reaction are indicated next to the arrows. Abbreviations: HCHO, formaldehyde; MDH, methanol dehydrogenase; MaDH, methylamine dehydrogenase; dH4MPT, dephosphotetrahydromethanopterin; Fae, formaldehyde-activating enzyme; CH2=dH4MPT, methylene-dH4MPT; MtdB and MtdA, methylene-tetrahydromethanopterin dehydrogenases; CH dH4MPT, methenyl-dephosphoH4MPT; Mch, methenyl-dH4MPT cyclohydrolase; CHO—dH4MPT, formyl-dH4MPT; Fhc, formyltransferase/hydrolase complex; Fdh, formate dehydrogenase; FtfL, formate-tetrahydrofolate ligase; H4F, tetrahydrofolate; CHO—H4F, to formyl-H4F; Fch, methenyl-H4F cyclohydrolase; CH
dH4MPT, methenyl-dephosphoH4MPT; Mch, methenyl-dH4MPT cyclohydrolase; CHO—dH4MPT, formyl-dH4MPT; Fhc, formyltransferase/hydrolase complex; Fdh, formate dehydrogenase; FtfL, formate-tetrahydrofolate ligase; H4F, tetrahydrofolate; CHO—H4F, to formyl-H4F; Fch, methenyl-H4F cyclohydrolase; CH H4F, methenyl-H4F; CH2—H4F, methylene-H4F; GSH, glutathione; GMA synthetase, gamma-glutamylmethylamide synthetase; NMG synthase, N-methyl glutamate synthase; NMG dehydrogenase, N-methyl glutamate dehydrogenase; FlhA, GSH/NAD-dependent formaldehyde dehydrogenase; FghA, S-formyl-GSH hydrolase. The dashed line represents the proposed NMG pathway, where “(i)” represents gamma-glutamylmethylamide and “(ii)” represents N-methyl glutamate. Gray lines represent the heterologous Paracoccus denitrificans formaldehyde detoxification pathway encoded on the plasmid pCM106 (16).
H4F, methenyl-H4F; CH2—H4F, methylene-H4F; GSH, glutathione; GMA synthetase, gamma-glutamylmethylamide synthetase; NMG synthase, N-methyl glutamate synthase; NMG dehydrogenase, N-methyl glutamate dehydrogenase; FlhA, GSH/NAD-dependent formaldehyde dehydrogenase; FghA, S-formyl-GSH hydrolase. The dashed line represents the proposed NMG pathway, where “(i)” represents gamma-glutamylmethylamide and “(ii)” represents N-methyl glutamate. Gray lines represent the heterologous Paracoccus denitrificans formaldehyde detoxification pathway encoded on the plasmid pCM106 (16).
