Fig 3.
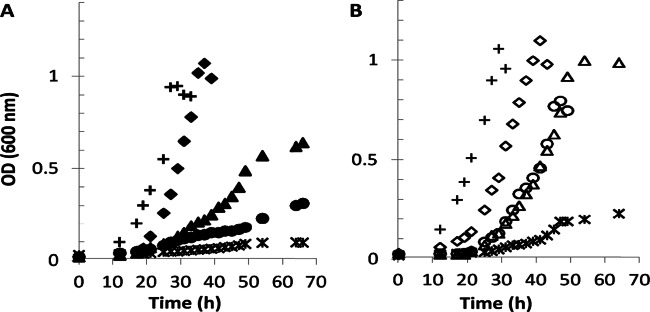
Formaldehyde accumulation reduces growth of the mtdB mutant strain in methylamine medium. (A) Growth of wild-type M. extorquens (crosses), mtdB mutant (triangles), msgA mutant (diamonds), mptG (encoding the first gene product necessary for dH4MPT biosynthesis) mutant (asterisks), and mtdB msgA double mutant (circles), all carrying the plasmid pCM80 as the vector control. All strains were pregrown on succinate and inoculated in medium containing methylamine (35 mM). (B) Growth of the same strains (represented by the same symbols but open instead of solid) under the same conditions, carrying the heterologous GSH-dependent formaldehyde oxidation system [pCM106 (fghA flhA)].
