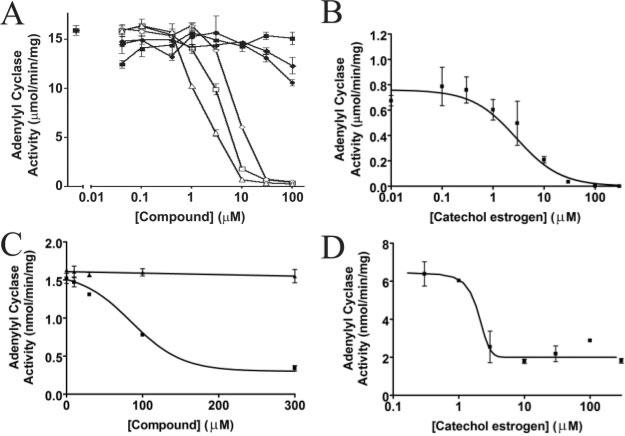
Fig. 2. Inhibition of CyaC and mammalian tmACs by catechol estrogens.
A, inhibition of purified recombinant human sAC enzyme by catechol estrogens. 2-CE (◇), 4-CE (△), and 2-hydroxy estrone (□) inhibit sAC with comparable affinity, whereas the parent compounds estrogen (◇) and estrone (■) as well as the metabolite 2-methoxy-2-CE (●) have no effect on sAC activity. B, inhibition of the cyanobacterial sAC homolog CyaC by 2-CE. The purified recombinant enzyme is inhibited with an IC50 of ~2 μm. C, dose-dependent inhibition of Sf9 cell membrane preparations containing human tmAC I by 2-CE. AC activity was assayed in duplicate in the presence of the indicated concentration of 2-CE (■) or estrogen (▲). D, inhibition of the purified soluble catalytic domains of human tmAC VII by CE. The tmAC VII activity is inhibited by 2-CE with an IC50 in the low micromolar range.