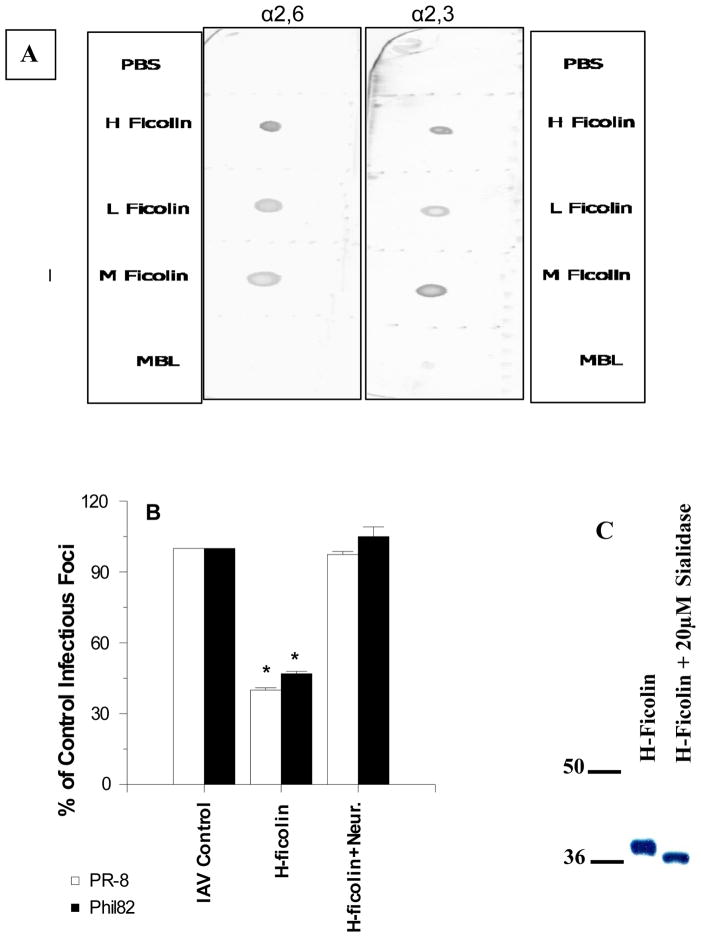
Figure 7. Presence of α(2,3) or α(2,6)-linked sialic acids on recombinant ficolins and effect of neuraminidase treatment of H-ficolin on antiviral activity.
In panel A, the presence of α(2,3) or α(2,6)-linked sialic acids on recombinant H-, L-, and M-ficolins was assessed by lectin blotting using SNA and MAA as sialic acid detecting molecules as described in methods. For comparison, MBL (which has no N-linked oligosaccharide attachments) was tested as well. In panel B, untreated H-ficolin, neuraminidase treated H-ficolin, or neuraminidase alone was pre-incubated with PR-8 or Phil82 IAV followed by infection of MDCK cells with the virus samples and infectious focus assay. Only untreated H-ficolin significantly inhibited viral infectivity (* indicates p<0.01 vs control). Panel C shows SDS-PAGE of untreated and neuraminidase treated H-ficolin. Results in panel B are mean±SEM of 4 experiments.