Abstract
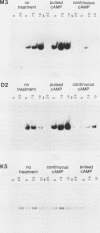
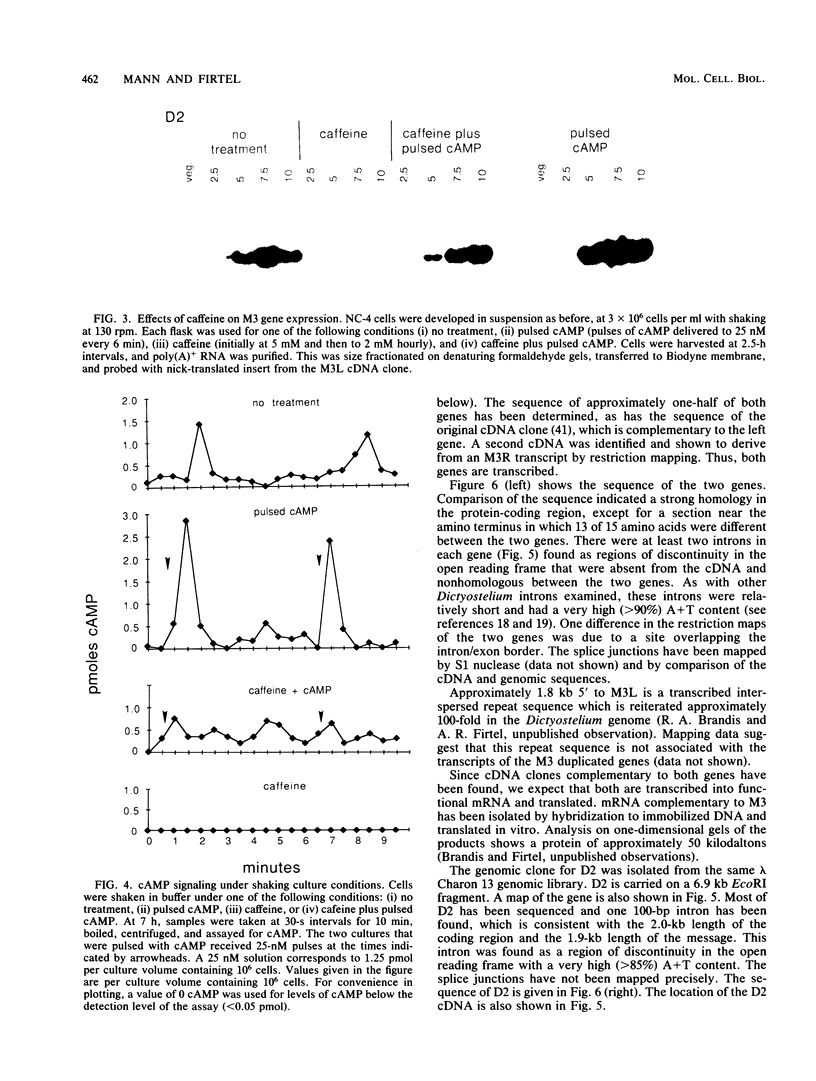
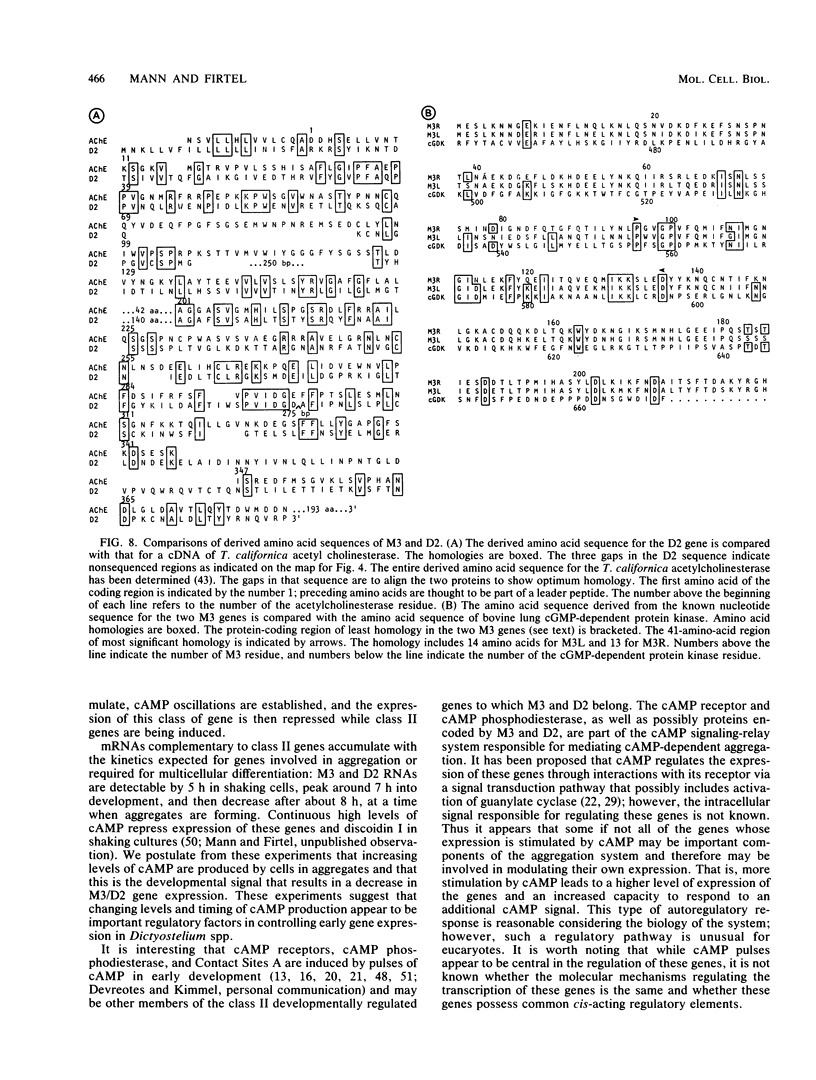
We examined two sets of genes expressed early in the developmental cycle of Dictyostelium discoideum that appear to be regulated by cyclic AMP (cAMP). The transcripts of both sets of genes were not detectable in vegetative cells. During normal development on filter pads, RNA complementary to these genes could be detected at about 2 h, peaked around 6 to 8 h, and decreased gradually thereafter. Expression of these genes upon starvation in shaking culture was stimulated by pulsing the cells with nanomolar levels of cAMP, a condition that mimics the in vivo pulsing during normal aggregation. Expression was inhibited by caffeine or by continuous levels of cAMP, a condition found later in development when in vivo expression of these genes decreased. The inhibition of caffeine could be overcome by pulsing cells with cAMP. These results suggest that the expression is mediated via the cell surface cAMP receptor, but does not require a rise in intracellular cAMP. mRNA from a gene of the second class was induced upon starvation, peaked by 2.5 h of development, and then declined. In contrast to the other genes, its expression was maintained by continuous levels of cAMP and repressed by cAMP pulses. These and other results on a number of classes of developmentally regulated genes indicates that changing levels of cAMP, acting via the cell surface cAMP receptor, are involved in controlling these groups of genes. We also examined the structure and partial sequence of the cAMP pulse-induced genes. The two tandemly duplicated M3 genes were almost continuously homologous over the sequenced portion of the protein-coding region except for a region near the N-terminal end. The two M3 genes had regions of homology in the 5' flanking sequence and showed slight homology to the same regions in gene D2, another cAMP pulse-induced gene. D2 showed extremely significant homology over its entire sequenced length to an acetylcholinesterase. The results presented here and by others suggest that expression of many early genes in D. discoideum is regulated via the cell surface cAMP receptor. We expect that many of these genes may play essential roles in early Dictyostelium development and could code for elements of the cAMP signal transduction pathway involved in aggregation.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barklis E., Lodish H. F. Regulation of dictyostelium discoideum mRNAs specific for prespore or prestalk cells. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1139–1148. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90297-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berlot C. H., Spudich J. A., Devreotes P. N. Chemoattractant-elicited increases in myosin phosphorylation in Dictyostelium. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):307–314. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90036-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner M., Thoms S. D. Caffeine blocks activation of cyclic AMP synthesis in Dictyostelium discoideum. Dev Biol. 1984 Jan;101(1):136–146. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(84)90124-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung S., Landfear S. M., Blumberg D. D., Cohen N. S., Lodish H. F. Synthesis and stability of developmentally regulated dictyostelium mRNAs are affected by cell--cell contact and cAMP. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):785–797. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90104-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datta S., Firtel R. A. Identification of the sequences controlling cyclic AMP regulation and cell-type-specific expression of a prestalk-specific gene in Dictyostelium discoideum. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):149–159. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datta S., Gomer R. H., Firtel R. A. Spatial and temporal regulation of a foreign gene by a prestalk-specific promoter in transformed Dictyostelium discoideum. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Mar;6(3):811–820. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.3.811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dicou E., Brachet P. A separate phosphodiesterase for the hydrolysis of cyclic guanosine 3',5'-monophosphate in growing Dictyostelium discoideum amoebae. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Aug;109(2):507–514. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04822.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doolittle R. F. Similar amino acid sequences: chance or common ancestry? Science. 1981 Oct 9;214(4517):149–159. doi: 10.1126/science.7280687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng D. F., Johnson M. S., Doolittle R. F. Aligning amino acid sequences: comparison of commonly used methods. J Mol Evol. 1984;21(2):112–125. doi: 10.1007/BF02100085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Firtel R. A., Baxter L., Lodish H. F. Actinomycin D and the regulation of enzyme biosynthesis during development of Dictyostelium discoideum. J Mol Biol. 1973 Sep 15;79(2):315–327. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90008-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Firtel R. A., Bonner J. Characterization of the genome of the cellular slime mold Dictyostelium discoideum. J Mol Biol. 1972 May 28;66(3):339–361. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90419-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerisch G., Fromm H., Huesgen A., Wick U. Control of cell-contact sites by cyclic AMP pulses in differentiating Dictyostelium cells. Nature. 1975 Jun 12;255(5509):547–549. doi: 10.1038/255547a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerisch G., Hess B. Cyclic-AMP-controlled oscillations in suspended Dictyostelium cells: their relation to morphogenetic cell interactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 May;71(5):2118–2122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.5.2118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosschedl R., Wasylyk B., Chambon P., Birnstiel M. L. Point mutation in the TATA box curtails expression of sea urchin H2A histone gene in vivo. Nature. 1981 Nov 12;294(5837):178–180. doi: 10.1038/294178a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juliani M. H., Brusca J., Klein C. cAMP regulation of cell differentiation in Dictyostelium discoideum and the role of the cAMP receptor. Dev Biol. 1981 Apr 15;83(1):114–121. doi: 10.1016/s0012-1606(81)80013-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimmel A. R., Carlisle B. A gene expressed in undifferentiated vegetative Dictyostelium is repressed by developmental pulses of cAMP and reinduced during dedifferentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2506–2510. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimmel A. R., Firtel R. A. Sequence organization in Dictyostelium: unique structure at the 5'-ends of protein coding genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jan 25;11(2):541–552. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.2.541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein C., Darmon M. Effects of cyclic AMP pulses on adenylate cyclase and the phosphodiesterase inhibitor of D. discoideum. Nature. 1977 Jul 7;268(5615):76–78. doi: 10.1038/268076a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein C., Juliani M. H. cAMP,-induced changes in cAMP-binding sites on D; discoideum amebae. Cell. 1977 Feb;10(2):329–335. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90227-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lappano S., Coukell M. B. Evidence that intracellular cGMP is involved in regulating the extracellular cAMP phosphodiesterase and its specific inhibitor in Dictyostelium discoideum. Dev Biol. 1982 Sep;93(1):43–53. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(82)90237-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrach H., Diamond D., Wozney J. M., Boedtker H. RNA molecular weight determinations by gel electrophoresis under denaturing conditions, a critical reexamination. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 18;16(21):4743–4751. doi: 10.1021/bi00640a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mato J. M., Krens F. A., van Haastert P. J., Konijn T. M. 3':5'-cyclic AMP-dependent 3':5'-cyclic GMP accumulation in Dictyostelium discoideum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jun;74(6):2348–2351. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.6.2348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKeown M., Firtel R. A. Differential expression and 5' end mapping of actin genes in Dictyostelium. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):799–807. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90105-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McRobbie S. J., Newell P. C. A new model for chemotactic signal transduction in Dictyostelium discoideum. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Sep 28;123(3):1076–1083. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(84)80243-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehdy M. C., Firtel R. A. A secreted factor and cyclic AMP jointly regulate cell-type-specific gene expression in Dictyostelium discoideum. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Apr;5(4):705–713. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.4.705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehdy M. C., Ratner D., Firtel R. A. Induction and modulation of cell-type-specific gene expression in Dictyostelium. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):763–771. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90062-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nellen W., Silan C., Firtel R. A. DNA-mediated transformation in Dictyostelium discoideum: regulated expression of an actin gene fusion. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;4(12):2890–2898. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.12.2890. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poole S. J., Firtel R. A. Conserved structural features are found upstream from the three co-ordinately regulated discoidin I genes of Dictyostelium discoideum. J Mol Biol. 1984 Jan 15;172(2):203–220. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(84)80038-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poole S., Firtel R. A., Lamar E., Rowekamp W. Sequence and expression of the discoidin I gene family in Dictyostelium discoideum. J Mol Biol. 1981 Dec 5;153(2):273–289. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90278-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reymond C. D., Gomer R. H., Mehdy M. C., Firtel R. A. Developmental regulation of a Dictyostelium gene encoding a protein homologous to mammalian ras protein. Cell. 1984 Nov;39(1):141–148. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90199-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romans P., Firtel R. A. Organization of the Dictyostelium discoideum actin multigene family. Flanking sequences show subfamily homologies and unusual dyad symmetries. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jun 5;183(3):311–326. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90003-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romans P., Firtel R. A., Saxe C. L., 3rd Gene-specific expression of the actin multigene family of Dictyostelium discoideum. J Mol Biol. 1985 Nov 20;186(2):337–355. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90109-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross F. M., Newell P. C. Streamers: chemotactic mutants of Dictyostelium discoideum with altered cyclic GMP metabolism. J Gen Microbiol. 1981 Dec;127(2):339–350. doi: 10.1099/00221287-127-2-339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowekamp W., Firtel R. A. Isolation of developmentally regulated genes from Dictyostelium. Dev Biol. 1980 Oct;79(2):409–418. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(80)90126-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowekamp W., Poole S., Firtel R. A. Analysis of the multigene family coding the developmentally regulated carbohydrate-binding protein discoidin-I in D. discoideum. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):495–505. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90636-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaap P., van Driel R. V. Induction of post-aggregative differentiation in Dictyostelium discoideum by cAMP. Evidence of involvement of the cell surface cAMP receptor. Exp Cell Res. 1985 Aug;159(2):388–398. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4827(85)80012-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schumacher M., Camp S., Maulet Y., Newton M., MacPhee-Quigley K., Taylor S. S., Friedmann T., Taylor P. Primary structure of Torpedo californica acetylcholinesterase deduced from its cDNA sequence. 1986 Jan 30-Feb 5Nature. 319(6052):407–409. doi: 10.1038/319407a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takio K., Wade R. D., Smith S. B., Krebs E. G., Walsh K. A., Titani K. Guanosine cyclic 3',5'-phosphate dependent protein kinase, a chimeric protein homologous with two separate protein families. Biochemistry. 1984 Aug 28;23(18):4207–4218. doi: 10.1021/bi00313a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Haastert P. J., Van Der Meer R. C., Konijn T. M. Evidence that the rate of association of adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate to its chemotactic receptor induces phosphodiesterase activity in Dictyostelium discoideum. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jul;147(1):170–175. doi: 10.1128/jb.147.1.170-175.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk B., Derbyshire R., Guy A., Molko D., Roget A., Téoule R., Chambon P. Specific in vitro transcription of conalbumin gene is drastically decreased by single-point mutation in T-A-T-A box homology sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7024–7028. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. G., Tsang A. S., Mahbubani H. A change in the rate of transcription of a eukaryotic gene in response to cyclic AMP. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7171–7175. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeh R. P., Chan F. K., Coukell M. B. Independent regulation of the extracellular cyclic AMP phosphodiesterase-inhibitor system and membrane differentiation by exogenous cyclic AMP in Dictyostelium discoideum. Dev Biol. 1978 Oct;66(2):361–374. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(78)90245-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]