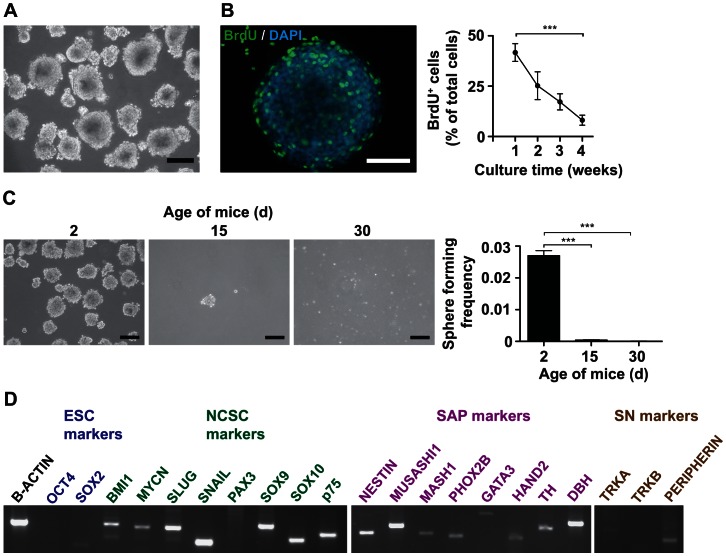
Figure 4. Postnatal mouse adrenal glands contain sphere-forming cells expressing markers of NCSCs and SAPs.
Mouse adrenals were dissociated to single cells and cultured using differential plating in low-attachment plastic dishes with serum-free medium containing bFGF and EGF. (A) Dissociated postnatal mouse adrenal glands form spheres in non-adherent serum-free conditions. Phase contrast image of spheres derived from the adrenal glands of a 2 d old mouse growing in suspension culture. Scale bar equals 200 µm. (B) Early spheres contain proliferating cells. BrdU was added to the culture medium of spheres at different time of culture. 24 h later BrdU was detected by immunofluorescence microscopy. Micrograph of a sphere cultured for 7 d stained with anti-BrdU and DAPI is shown in the left panel, scale bar equals 50 µm. Quantification of BrdU-incorporating sphere cells is depicted in the right panel. The means of two independent experiments are shown (15 wells/time-point). Statistical analysis was performed using the t-test. ***, p<0.001. (C) Frequency of sphere forming cells decreases with age of mice. 1.2×105 cells/ml derived from adrenal glands of mice of increasing age were seeded in non-adherent serum-free condition. Phase contrast images of spheres are shown, scale bar equals 200 µm. Sphere-forming frequency was calculated as frequency of spheres formed per number of cells seeded (histogram). The means of three independent experiments are shown. Statistical analysis was performed using the t-test. ***, p<0.001. (D) Sphere cells express markers of SAPs and NCSCs. RT-PCR analysis was performed on RNA isolated from adrenal-derived spheres.