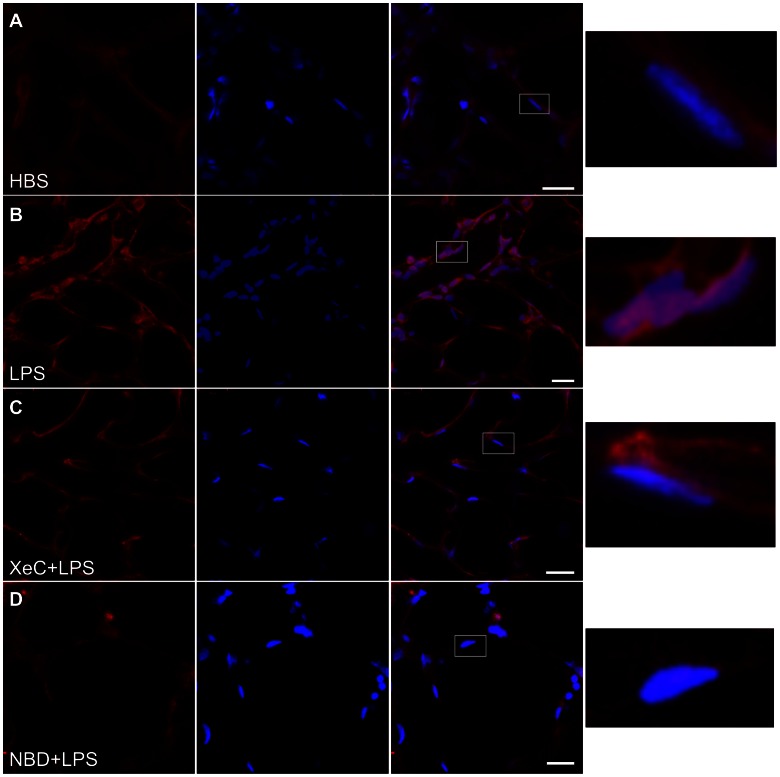
Figure 6. Nuclear localization of NF-kB.
Confocal images show immunofluorescence of NF-κB p65 subunit in lung microvessels (red, left column), fluorescence of the nuclear marker Hoechst-33342 (blue, column 2) and merge (column 3) for the indicated treatments. Pink color in the merged images indicates colocalization of NF-κB immunofluorescence and nuclear marker fluorescence. Treatment durations were as outlined in Methods. Nuclear localization of NF-κB immunofluorescence in the region marked by the rectangles (column 3 images) is shown magnified on far right column. Again, pink color indicates localization of NF-κB immunofluorescence (red) and nuclear marker fluorescence (blue). Treatment groups repeated in 3 lungs, except for NBD treatment group (n = 1). Note the higher colocalization in LPS-treated microvessels (B), compared to HBS-treated (A), and XeC- (C) and NBD-pretreated microvessels. NBD = IKK-NBD.