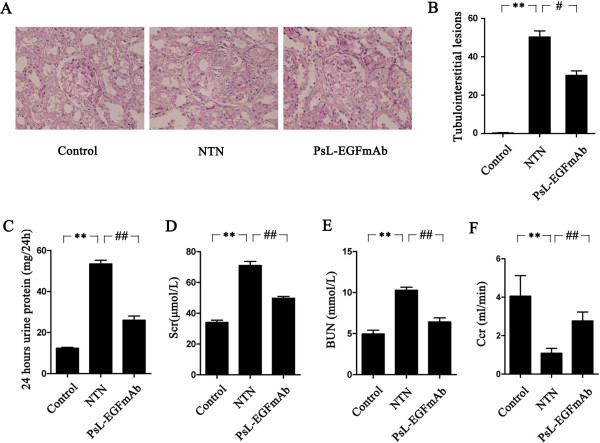
Figure 1.
Effect of PsL-EGFmAb on renal pathology and function. A, PAS staining of renal tissues and corresponding quantification (final magnification × 200). Renal tissues were harvested on day 14. B, Tubulointerstitial damage was evaluated according to the scoring system we mentioned in the Methods. C-F, Twenty-four-hour urine proteins (C), Scr (D) and BUN (E) of nephritic rats were significantly elevated, whereas CCr (F) levels were significantly reduced on day 14 compared with non-nephritic controls (p < 0.01). PsL-EGFmAb treatment significantly reduced twenty-four-hour urine proteins (C), Scr (D), BUN (E) levels and increased CCr (F) compared with NTN group (p < 0.01), indicating improvement of renal function after PsL-EGFmAb treatment. The mean ± SD of three independent experiments is shown. **p < 0.01 vs. control; #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01 vs. NTN group.