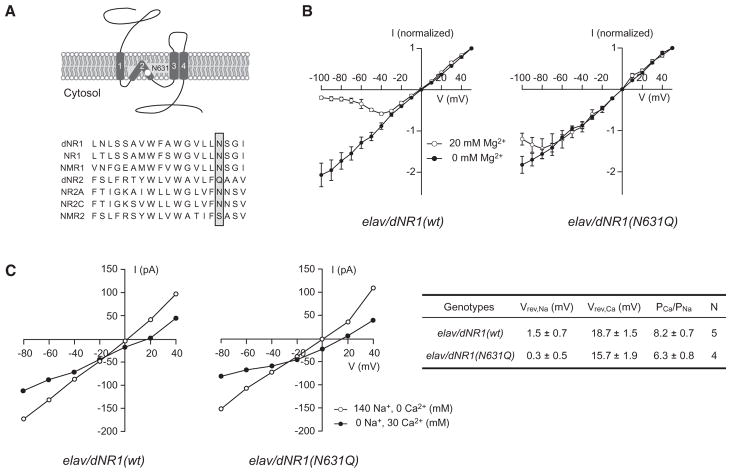
Figure 2. Suppression of dNMDAR Mg2+ Block in Neurons from Transgenic Pupae Overexpressing dNR1(N631Q).
(A) Schematic diagram of dNR1 and amino acid sequence comparisons of the TM2 domains of Drosophila (dNR1 and dNR2), mouse (NR1, NR2A, and NR2C), and C. elegans (NMR1 and NMR2) NMDAR subunits. The white circle (upper) and shadowed box (lower) indicate the Mg2+ block site in the TM2 domain.
(B) Current-voltage (I-V) curves generated from neurons from elav/dNR1(wt) (n = 6) and elav/dNR1(N631Q) pupae (n = 6). Currents elicited by 100 μM NMDA were normalized to peak responses at +50 mV. Due to Mg2+ block, all examined neurons from elav/dNR1(wt) displayed a typical J-shaped I-V relation in the presence of 20 mM extracelluar Mg2+.
(C) (Left) I-V relationships in high Na+ (open circle) and high Ca2+ (closed circle) extracellular solutions for elav/dNR1(wt) and elav/dNR1(N631Q) neurons. I-V relationships in each extracellular solution were recorded from the same neuron after confirming the presence [for elav/dNR1(wt)] or absence [for elav/dNR1(N631Q)] of Mg2+ block. (Right) Reversal potentials in high Na+ extracellular solution (Vrev,Na) and in high Ca2+ extracellular solution (Vrev,Ca) were measured from the left panel, and relative Ca2+ permeabilities (PCa/PNa) were calculated using the Goldman-Hodgkin-Katz (GHK) equation.
See also Figures S2 and S3.