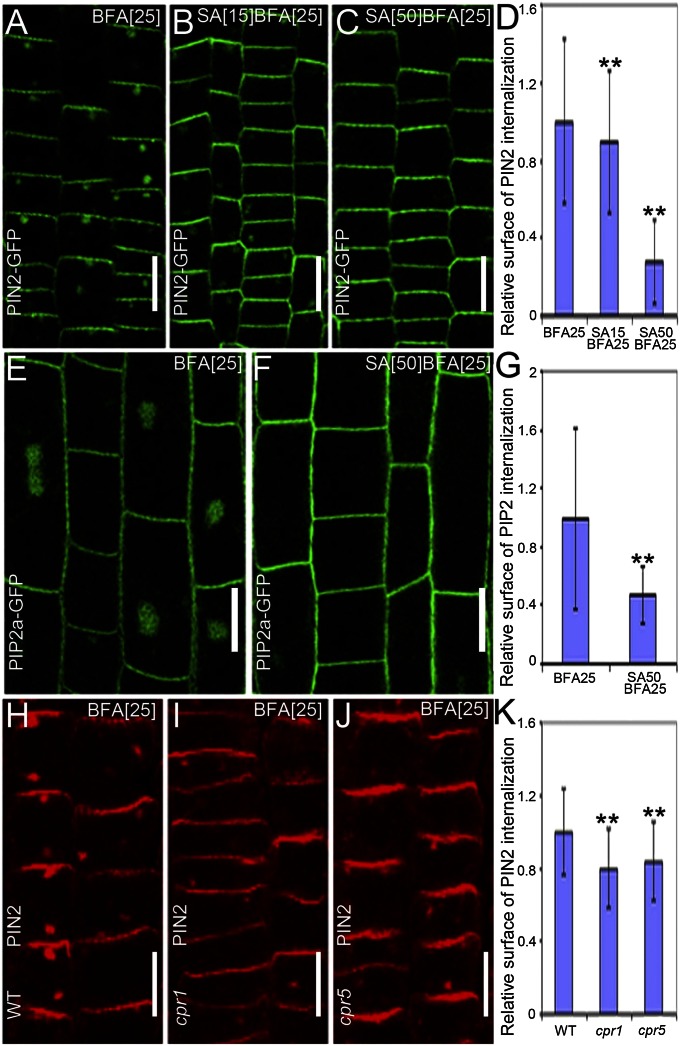
Fig. 1.
SA interferes with the BFA-visualized internalization of PM proteins. (A–C) PIN2-GFP localization in young epidermal root cells treated with 25 μM BFA for 90 min (n = 215 BFA bodies; 12 roots) (A) or cotreated with either 15 μM SA (n = 262 BFA bodies; 14 roots) (B) or 50 μM SA (n = 25 BFA bodies; 16 roots) (C) for 90 min, after a 30-min SA pretreatment. (D) Quantification of the relative surface of the internalized PIN2-GFP in A–C. (E and F) PIP2a-GFP localization in elongated root epidermal cells after treatment with 25 μM BFA for 90 min (n = 257 BFA bodies; 15 roots) (E) or cotreated with 50 μM SA for 90 min after pretreatment with 50 μM SA for 30 min (n = 86 BFA bodies; 27 roots) (F). (G) Quantification of the relative surface of the internalized PIP2a-GFP in E and F. (H–J) Immunolocalization of PIN2 in young epidermal root cells of WT (Col-0) (n = 430 BFA bodies; 23 roots) (H), cpr1 (n = 258 BFA bodies; 14 roots) (I), and cpr5 (n = 237 BFA bodies; 12 roots) (J) mutants after treatment with 25 μM BFA for 90 min. (K) Quantification of the relative surface of the internalized PIN2 in H–J. Values in D, G, and K are mean surface areas normalized to the respective control treatments. Data are means ± SD; **P < 0.01 (Student t test). (Scale bars: 10 µm).