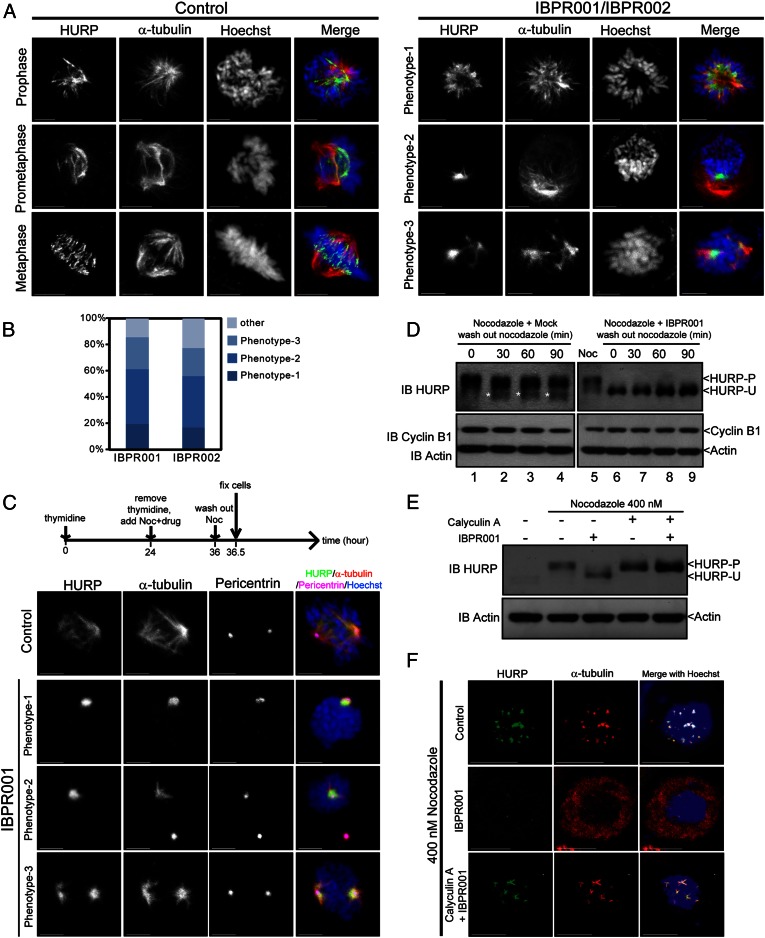
Fig. 4.
IBPR compounds restrict the association of HURP with centrosomal microtubules. (A) Representative HURP morphological phenotypes in HeLa cells treated with DMSO control (Left) or 1.0 μM of IBPR001/IBPR002 (Right) for 13 h following thymidine release. Cells were coimmunostained with rabbit anti-HURP and mouse anti–α-tubulin antibodies. DNA was stained with Hoechst33342. (B) Statistics of the representative HURP morphological phenotypes presented in A. (C) Cells were treated as shown in the upper scheme. HURP is associated with centrosomal microtubules (stained with α-tubulin) emanating from centrosomes (stained with Pericentrin) in IBPR001-treated cells upon nocodazole removal. Images are summations of z-stacks. (Scale bars: 5 μm.) (D) Cells were treated as in the upper scheme in C. Cell lysates were harvested every 30 min after the removal of nocodazole. Immunoblots of cyclin B1 and actin were included to indicate the cell-cycle status and serve as a loading control, respectively. The immunoblot of HURP shows that HURP remained unphosphorylated upon nocodazole removal (lanes 7–9). On the other hand, part of HURP was converted to the unphosphorylated form upon nocodazole removal in control cells (lanes 2–4, denoted by asterisks). (E) Immunoblot of HURP in nocodazole-arrested cells treated with 1.0 μM of IBPR001, 100 nM of Calyculin A, or both for 1 h. Immunoblot of actin was included as a loading control. (F) Cellular localization of HURP (green) and α-tubulin (red) in nocodazole-arrested cells treated with 1.0 μM of IBPR001 or cotreated with 1.0 μM of IBPR001 and 100 nM of Calyculin A. Cells were fixed after 1 h of drug treatment. A control cell (DMSO) is shown for comparison. Images are summation of z-stacks. (Scale bars: 5 μm.)