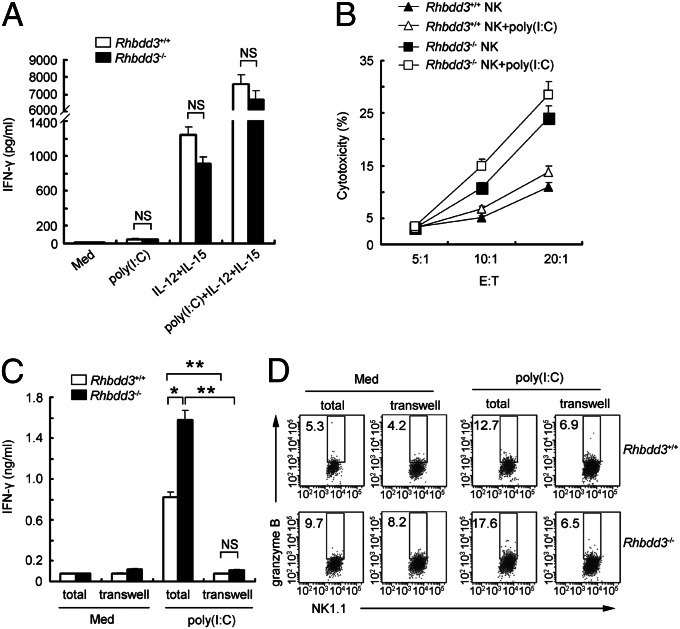
Fig. 2.
Accessory cells are required for the suppression of TLR3-triggered NK cell activation by Rhbdd3 in a cell–cell contact-dependent manner. (A) Rhbdd3+/+ and Rhbdd3−/− splenic NK cells were stimulated with poly(I:C), IL-12/15, or poly(I:C) plus IL-12/15, and IFN-γ levels in supernatants were assessed by CBA. (B) Rhbdd3+/+ and Rhbdd3−/− splenic NK cells were stimulated with poly(I:C) and then cultured with 5,6-carboxyfluorescein diacetate succinimidyl ester-labeled Yac-1 cells at indicated E:T ratios. The cytotoxicity of NK cells against YAC-1 cells were analyzed by FACS. (C and D) Splenic DX5+ NK cells and the left DX5− splenocytes, which were, respectively, seeded in the upper and lower compartments of the Transwell system (transwell), or total splenocytes (total) were stimulated with poly(I:C). IFN-γ levels in supernatants (C) and intracellular granzyme B in NK1.1+ cells (D) were respectively assessed by CBA and FACS. The data shown are the means ± SD (A–C) from three independent experiments. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; NS, not significant.