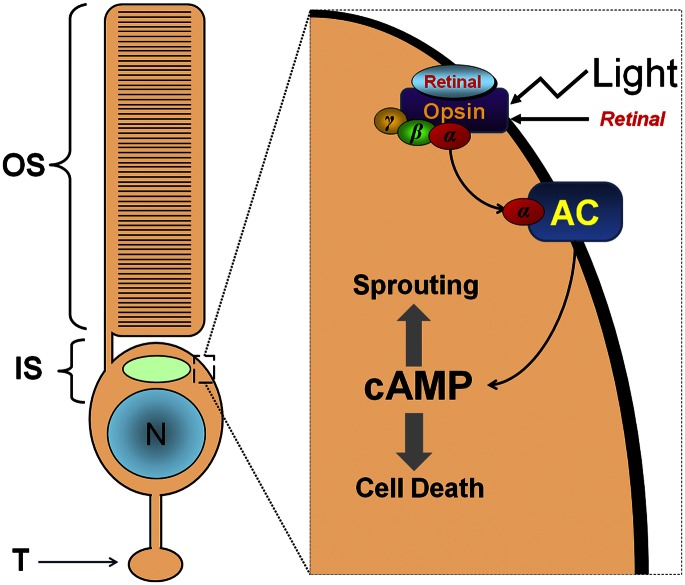
Fig. 1.
(Left) An intact rod photoreceptor cell. IS, inner segment; N, nucleus; OS, outer segment; T, terminal. (Right) A portion of the inner segment. In retinal disease, opsin, which normally is sequestered in the outer segment, appears on inner segment membranes. If bound by retinal and in the presence of light, opsin activates an abnormal signaling pathway involving adenylyl cyclase (AC) and leading to increased cAMP, neuritic sprouting, and cell death. Modified from (3), Copyright Association for Research in Vision and Ophthalmology.