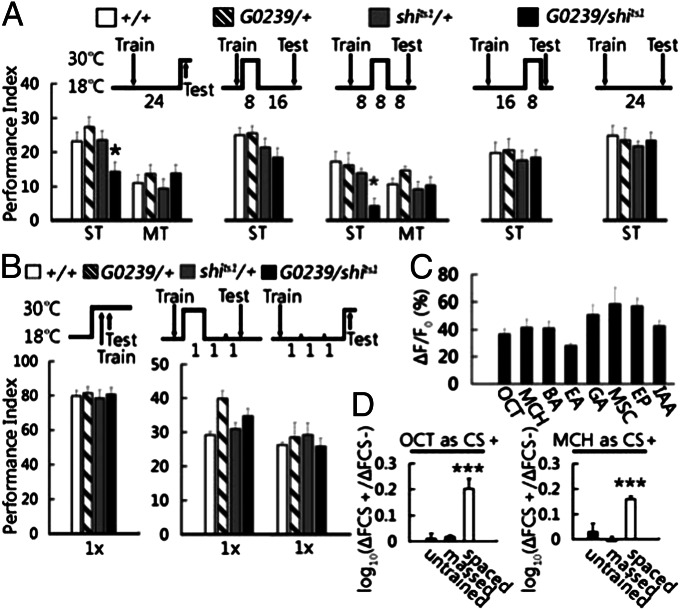
Fig. 2.
Neurotransmission and functional response of MB-V3 neurons during LTM formation. (A) Roles of MB-V3 neurotransmission on LTM. Blocking neurotransmission from MB-V3 neurons with temperature sensitive shits1 protein (30 °C) during retrieval (P = 0.015; n = 12) or 8–16 h after training (P = 0.012; n = 8) impaired 1-d memory after spaced training, but not after massed training. Blocking neurotransmission during 0–8 or 16–24 h after spaced training or keeping the shits1 flies in permissive temperature (18 °C) had no effect on 1-d memory. (B) Blocking neurotransmission from MB-V3 neurons during acquisition or 3 h after a single training session had no effects on memory retention. Values are means ± SEM (n = 8 for each group). (C) Neural activity in MB-V3 neurons in response to eight different odors (OCT, MCH, BA, EA, GA, MSC, EP, and IAA). Values are means ± SEM (n ≧ 8 for each odor). (D) Enhanced neural activity in MB-V3 neurons in response to conditioned odors after spaced, but not massed, training. Values are means ± SEM (P < 0.001; n ≧ 8 for each group). For more details, please see SI Methods.