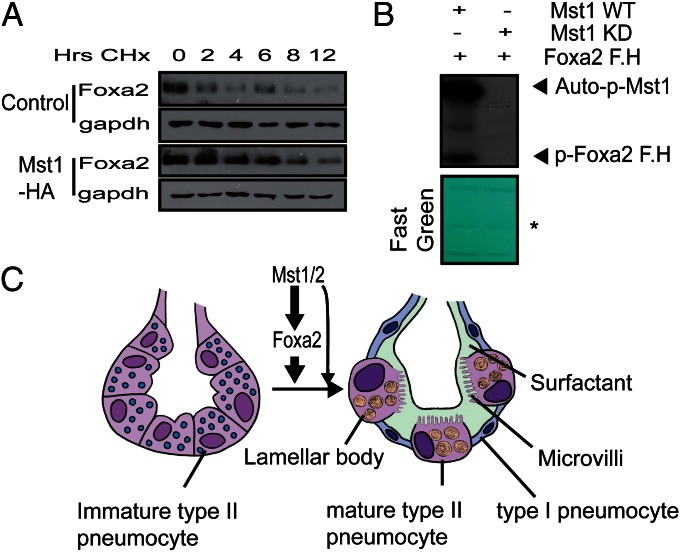
Fig. 5.
Mst1 increases the stability of Foxa2 protein and phosphorylates the forkhead domain of Foxa2. (A) A549 cells were infected with empty (control) or Mst1-HA–expressing retrovirus. The stability of endogenous Foxa2 protein with and without Mst1 overexpression was measured in cells in which new protein synthesis was inhibited with cycloheximide (30 μg/mL). Cells were harvested at the indicated times after addition of cycloheximide and analyzed for Foxa2 by Western blotting. Relative protein levels were compared with 0-h time points. (B) In vitro kinase assays. Anti-Flag immunoprecipitates prepared from 293T cell lysates expressing Flag-tagged WT or kinase-dead (KD) MST1 were assayed for kinase activity. GST fused with the forkhead domain of Foxa2 was used as a substrate. After autoradiography, the membrane was stained with Fast Green to reveal substrate input (Lower). *Ig heavy chain. (C) Schematic model of Mst1/2 and Foxa2 regulation of peripheral lung maturation. Mst1/2 and Foxa2 regulate type 2 pneumocytes to differentiate and produce lamellar bodies, surfactant, and microvilli. The differentiation of type II pneumocytes to type I pneumocytes requires Mst1/2 and Foxa2 signals.