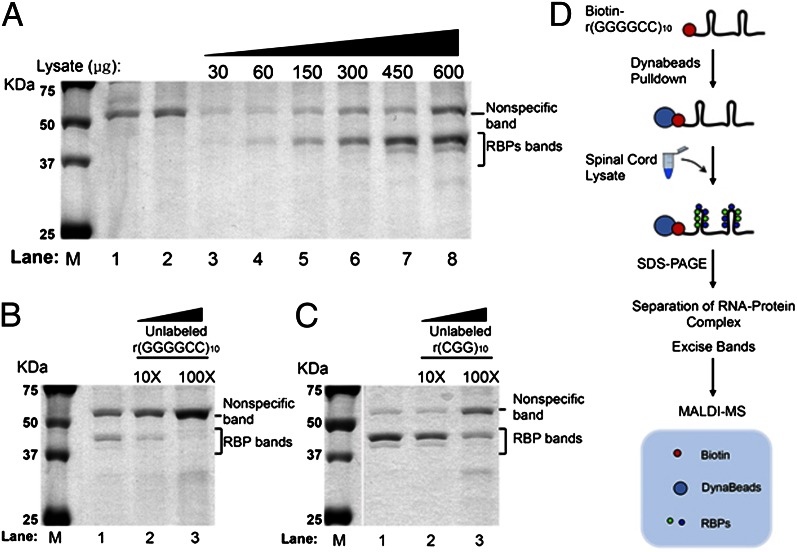
Fig. 3.
Identification of rGGGGCC RBPs. (A) GGGGCC RNA-binding assays with mouse spinal cord lysates. Biotinylated r(GGGGCC)10 repeat was incubated with increasing concentrations of mouse spinal cord lysates. Lane M refers to the molecular weight marker in all blots. Lane 1, 600 µg of spinal cord lysate only; lane 2, 300 µM biotin incubated with 600 µg of spinal cord lysate; lanes 3–8, 300 µM biotinylated r(GGGGCC)10 repeat incubated with 30, 60, 150, 300, 450, and 600 µg of spinal cord lysate. (B) rGGGGCC repeat RBP competition assay with excess unlabeled r(GGGGCC)10 repeat. Lane 1, 300 µM biotinylated r(GGGGCC)10 repeat only; lane 2, 300 µM biotinylated r(GGGGCC)10 repeat and 10× r(GGGGCC)10 repeat; lane 3, 300 µM biotinylated r(GGGGCC)10 repeat and 100× r(GGGGCC)10 repeat. All lanes were incubated with 300 µg of spinal cord lysate. (C) rGGGGCC repeat RBP competition assay with excess unlabeled r(CGG)10 repeat. Lane 1, 300 µM biotinylated r(GGGGCC)10 repeat only; lane 2, 300 µM biotinylated r(GGGGCC)10 repeat and 10× r(CGG)10 repeat; lane 3, 300 µM biotinylated r(GGGGCC)10 repeat and 100× r(CGG)10 repeat. All lanes were incubated with 300 µg of spinal cord lysate. (D) Work flow schematic for identification of RBPs by MS.