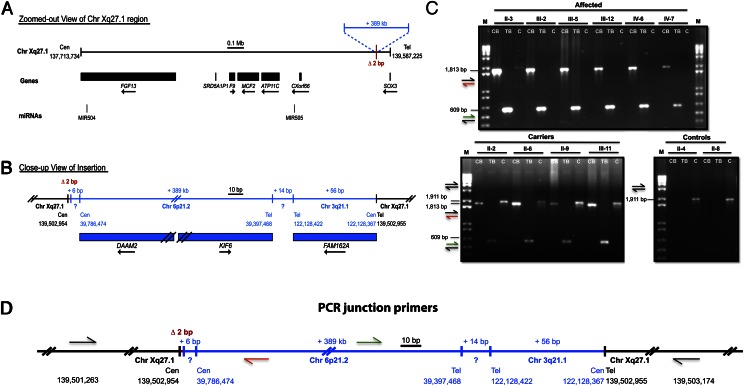
Fig. 3.
Whole-genome sequencing revealed a 389-kb interchromosomal insertion at Xq27.1 that cosegregates with the X-linked hypertrichosis phenotype. (A) Chromosome Xq27.1 in X-linked hypertrichosis. The genes and microRNAs encoded in the surrounding region are shown as black boxes with arrows indicating the direction of transcription. (B) WGS was used to determine the breakpoints and content of the interchromosomal insertion (shown in blue), including the 386-kb duplication from chromosome 6p21.2, 14 bp of unknown origin, and 56 bp of chromosome 3q21.2. (C) PCR amplification of the centromeric and telomeric junctions of the insertion on DNA from control, carrier, and affected individuals demonstrated segregation of the X-linked phenotype in the family at the genomic level. CB, TB, and C represent centromeric breakpoint, telomeric breakpoint, and controls, respectively. M, marker (1 kb + ladder). (D) Primer design of the centromeric and telomeric junctions; colored arrows correspond to the amplicons produced as shown in C. All images are drawn to scale. Genomic coordinates reference the UCSC Genome Browser human reference genome build hg19.