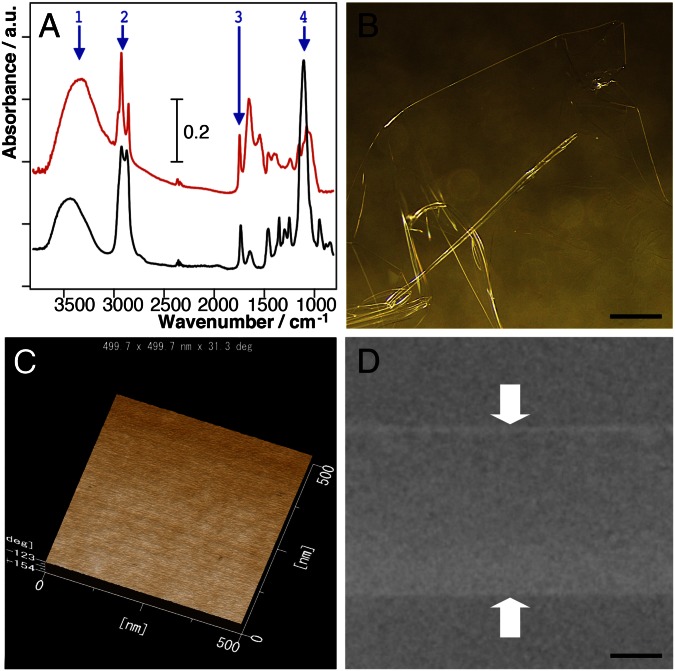
Fig. 3.
(A) Investigation of natural and synthetic membranes with properties affording protection of living tissues against the effects of high vacuum. FTIR spectra indicate that both the ECS of Drosophila larvae (red line) and Tween 20 (black line) possess similar functional groups [1, υO–H (hydroxyl); 2, υC–H (alkyl); 3, υC = O (carboxyl); and 4, υC–O (ether or hydroxyl)]. Long alkyl chains are hydrophobic and hydroxyl, carboxyl, and ether groups are hydrophilic. (B–D) Newly synthesized Tween 20 membrane following plasma polymerization: the surface as observed by light microscopy (B), by AFM (C), and in vertical section by TEM (D). [Scale bars: 5 mm (B) and 2 µm (D).]