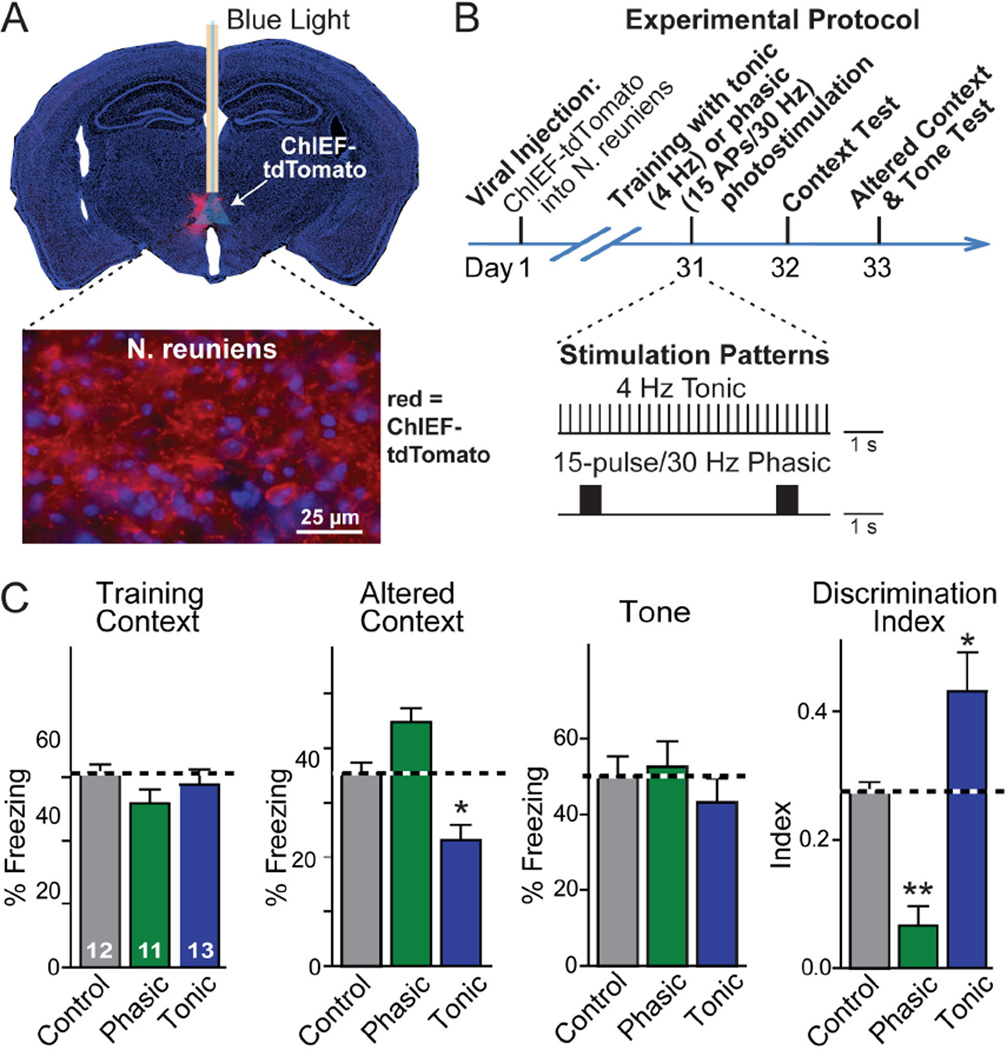
Fig. 4. Firing pattern of N. reuniens neurons dictates memory generalization.
A, Coronal brain section illustrating expression of ChIEF-tdTomato (red fluorescent channelrhodopsin) in the N. reuniens (top), and high-magnification micrograph showing ChIEF-tdTomato expressing N. reuniens neurons and their axonal fibers (bottom).
B, Experimental protocol for testing the effect of different optogenetic stimulation patterns of N. reuniens neurons on fear conditioning behavior, with the stimulation patterns illustrated below the time diagram. N. reuniens neurons were stimulated throughout the 6-min training period either by a 4 Hz tonic stimulation or a 30 Hz phasic stimulation, administered for 0.5 s every 5 seconds; stimulus light pulses were 15 ms.
C, Tonic and phasic optogenetic stimulation produced opposite effects on fear memory generalization. Control mice also expressed channelrhodopsin and contained an implanted optical fiber, but were not stimulated. Data shown are means ± SEMs; numbers in bars indicate number of mice analyzed. Statistical significance (* P<0.05; ** P<0.01) was assessed by two-way mixed-model ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s post-hoc test comparing the freezing levels, or by one-way ANOVA followed by Turkey’s post-hoc test for the discrimination index.