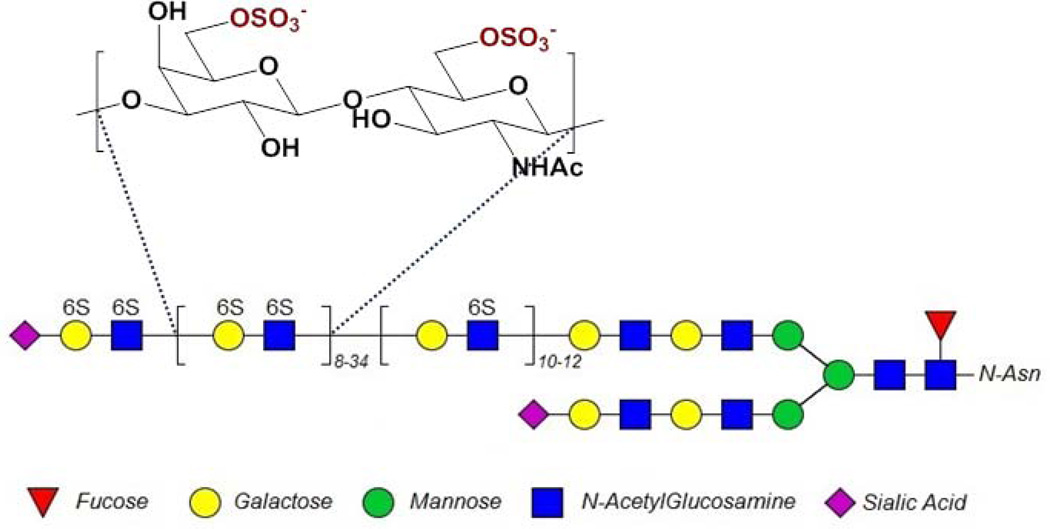
Figure 1.
Typical structure of corneal KS. The repeating galactose-glucosamine disaccharide structure shown here may be modified with 6-O-sulfo groups (as shown). KS chains are known to have a section of low sulfation (a single 6-O-sulfo group on the N-acetylglucosamine) close to the protein backbone and a section of higher sulfation (6-O-sulfo group on both N-acetylglucosamine and galactose) towards the chain’s non-reducing terminus (See references [4–7]), and are often capped by sialic acid (see reference [6]). In the cornea, KS is N-linked through an asparagine to one of three protein core structures, lumican, keratocan or mimecan.