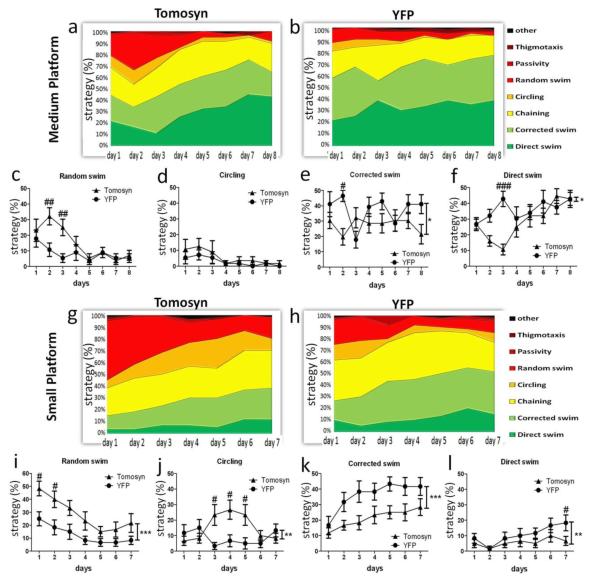
Figure 3. YFP-tomosyn1-overexpressing mice use swimming strategies of a lower cognitive ability compared to YFP-overexpressing mice during learning days under more stringent conditions in the MWM test.
When using the medium-sized platform (14 cm length), during learning days (a) YFP-tomosyn1-overexpressing mice used significantly higher levels of non-cognitive strategies compared to (b) YFP-overexpressing who used higher levels of high cognitive ability strategies. While YFP-tomosyn1-overexpressing mice used higher levels of (c) random swimming and (d) circling during days 2 and 3, YFP-overexpressing mice showed significantly higher levels of (e) corrected and (f) direct swim. More drastic differences were measured between (g) YFP-tomosyn1- and (h) YFP-overexpressing mice using the small-sized platform (12 cm length). YFP-tomosyn1-overexpressing mice used significantly higher levels of the low cognitive ability strategies (i) random swimming and (j) circling, while YFP-overexpressing mice used significantly higher levels of the high cognitive ability strategies (k) corrected and (l) direct swim. Graphs show percent of trials each swimming strategy was performed by mice per each day. Values are means±s.e.#P<0.05, ##P<0.01, ###P<0.001, *P<0.05, **P<0.005, ***P<0.0001