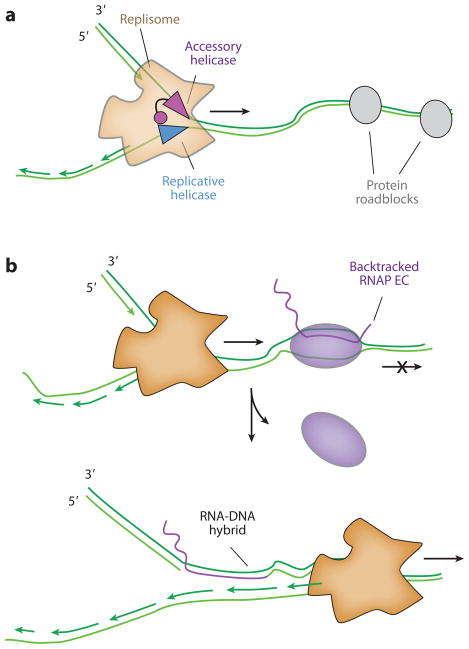
Figure 5.
(a) Accessory helicases interact with the replisome to remove protein roadblocks. In Escherichia coli, the C terminus of the accessory, nonreplicative Rep helicase physically interacts with DnaB. Accessory helicases can aid replication past protein roadblocks such as LacI repeats, hydrolytically inactive EcoRI, and head-on RNAP collisions. (b) Upon encountering a backtracked RNA polymerase (RNAP) in a codirectional orientation, the replisome can reinitiate from the 3′ end of the mRNA R-loop. A subsequent round of replication converts the resulting nick into a double-strand break. Abbreviation: EC, elongation complex.