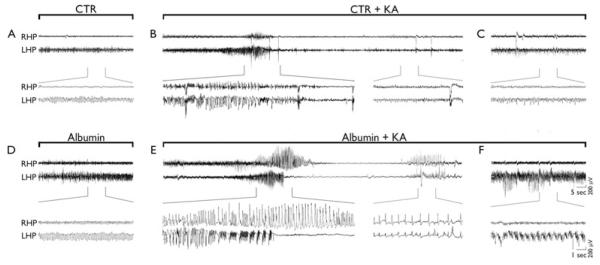
Figure 4.
Effects of rat albumin on baseline and KA-induced EEG activity in the hippocampus. Representative hippocampal EEG tracings in freely moving rats injected i.c.v. with dextran (CTR, A–C) or rat albumin (500 μg/4 μl) (D–F), either alone (A and D, respectively) or 24 h after KA (80 ng, intrahippocampally) (B, C and E, F, respectively). Panel A depicts EEG activity after dextran injection, which did not differ from preinjection baseline. Panel D depicts high-amplitude, high-frequency spiking activity (approximately 8 Hz) ipsilateral to albumin injection. This activity occurs within 15 min from injection, lasts for 60 min on average, and reverts to baseline within 2 h (see Fig. 5). Panels B and E depict a representative ictal episode recorded after KA injection in rats preinjected with dextran (B) or albumin (E). Panels C and F depict spiking activity during the third hour of recording after KA in rats preinjected with dextran (C) or albumin (F). Tracing enlargements are reported in brackets.
Epilepsia © ILAE