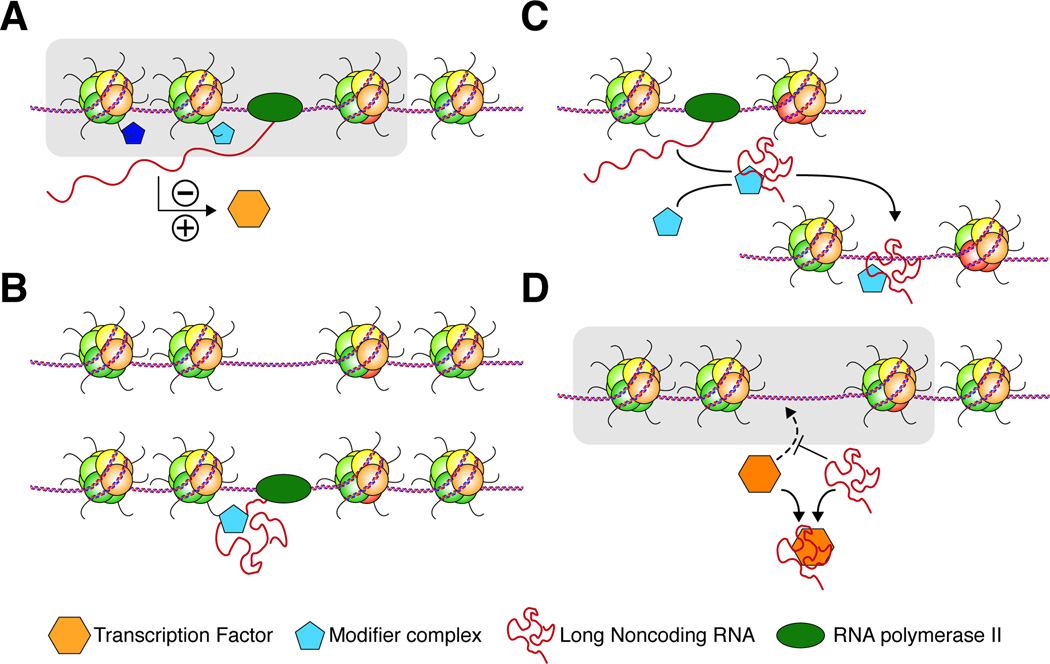
Figure 2. Functional modules of IncRNAs in the nucleus.
(A) The act of transcription at noncoding regions can modulate gene expression through the recruitment of chromatin modifiers to the site of transcription. These complexes can create a local chromatin environment that facilitates or blocks the binding of other regulators. (B) LncRNAs can function in cis, recruiting protein complexes to their site of transcription, thus creating a locus specific address. Cells can use this mechanism to repress gene or activate gene expression. (C) LncRNAs can function in trans and recruit protein complexes to chromatin loci away from their site of transcription. (D) LncRNAs can bind and sequester transcription factors away from their target chromosomal regions.