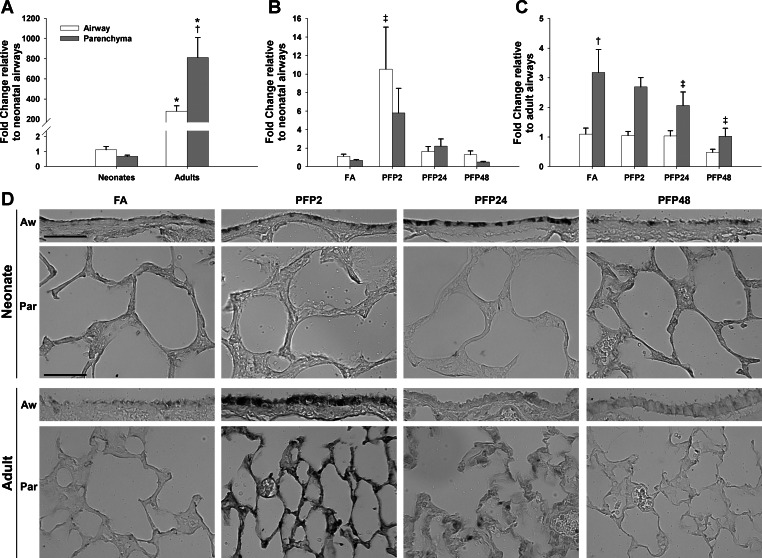
Fig. 4.
CYP1A1 compartmental mRNA and protein expression. RT-PCR expression in airway and parenchyma compartments in neonatal and adult rats exposed to PFPs. A: basal CYP1A1 mRNA levels were significantly higher in adults. Although no compartmental differences were observed in neonates, there was 4-fold more CYP1A1 in the parenchyma than in airways in adults. B: after PFP exposure, neonate CYP1A1 mRNA was transiently upregulated at PFP2 in the airways and reverted to FA levels by 24 h. C: a time-dependent decrease in CYP1A1 was observed in the adult parenchyma, reaching significance at 24 and 48 h postexposure. Data are presented as means + SE (n = 5–7 rats/group, in each compartment) *Significantly different compared with neonates in the same compartment. †Significantly different compared with airways in the same age. ‡Significantly different compared with FA in the same compartment. CYP1A1 immunohistochemical expression is presented in D. Although basal CYP1A1 was low in both ages across either lung compartment, CYP1A1 protein had different spatial and temporal patterns compared between neonates and adults after exposure. Neonatal CYP1A1 protein trailed mRNA levels, and CYP1A1 airway protein was enhanced at PFP24. CYP1A1 responded more acutely in adult animals, where staining was transiently observed in both lung compartments at PFP2. Scale bar is 50 μm.