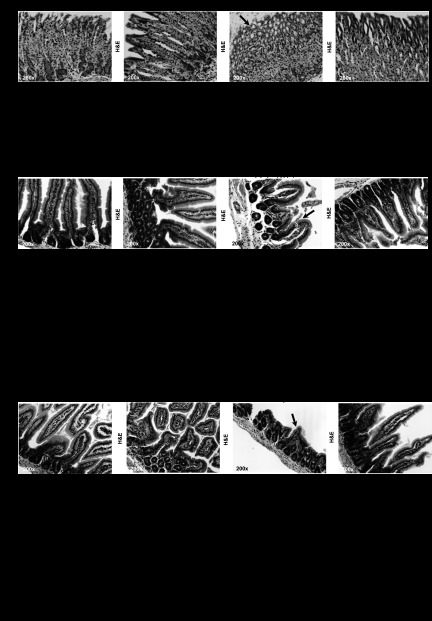
Fig. 1.
Milk osteopontin (m-OPN) preserves the stomach, duodenum, and jejunum architecture under ethanol consumption. Wild-type (WT) mice were fed 3 wk either the control or the alcohol Lieber-DeCarli diet alone or in combination with 200 μg/ml m-OPN. Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining from the stomach showed more erosion (arrow) in alcohol-treated than in cotreated mice (A). Structural changes were quantified as villus height, crypt depth, and gastric gland height (B). H&E staining showed more erosion (arrow) in the duodenum and jejunum in alcohol-treated than in m-OPN-cotreated mice (C and E). Structural changes in the duodenum and jejunum were quantified as villus height, crypt depth, and gland height. Crypt cell and enterocyte proliferation were quantified on Ki67 immunohistochemistry (IHC). The inflammation scores are also shown (D and F); n = 6 mice in each group. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001 for any alcohol-treated group vs. its own control. ●P < 0.05, ●●P < 0.01, and ●●●P < 0.001 for any m-OPN treated vs. its own control.