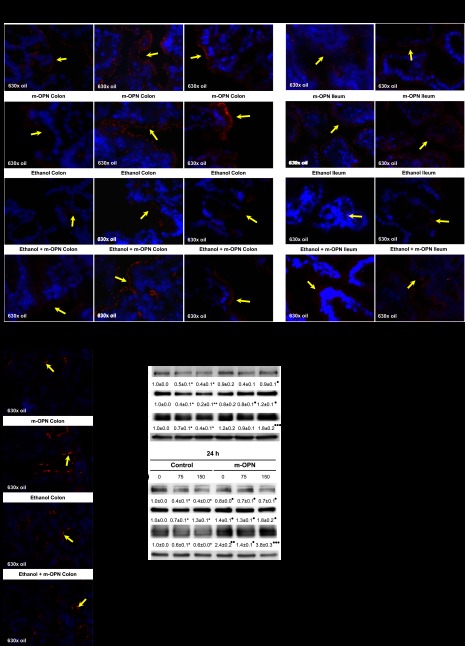
Fig. 2.
m-OPN maintains tight-junction protein expression in colon and ileum under ethanol consumption and preserves gut permeability. WT mice were fed 3 wk either the control or the alcohol Lieber-DeCarli diet alone or in combination with 200 μg/ml m-OPN. Immunofluorescence for tight-junction proteins was performed on frozen sections. Ethanol-treated mice showed loss of zonnula occludens-1 (ZO-1), occludin, and claudin-5 expression (yellow arrows) in colon (A) and occludin and claudin-5 in ileum (B), whereas m-OPN preserved the expression of all proteins in mice cotreated with ethanol. All groups of mice showed similar claudin-2 expression (yellow arrows) in the colon regardless of treatment (C). m-OPN preserves tight-junction protein expression in Caco-2 cells cotreated with ethanol. Caco-2 cells were coincubated with 0–150 mM ethanol in the presence of 0–50 nM m-OPN, and the expression of ZO-1, E-cadherin, and occludin was evaluated at 6 and 24 h by Western blot. Results are average values ± SE of arbitrary densitometry units over the control assigned a value of 1; n = 3. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01 for alcohol-treated vs. control. ●P < 0.05, ●●P < 0.01, and ●●●P < 0.001 for m-OPN cotreated vs. ethanol (D). m-OPN preserves gut permeability. Translocation of FITC-Dextran from the gut to the plasma was lower in m-OPN-cotreated than in ethanol-treated mice; n = 6. ●●●P < 0.001 for m-OPN treated vs. control (E).