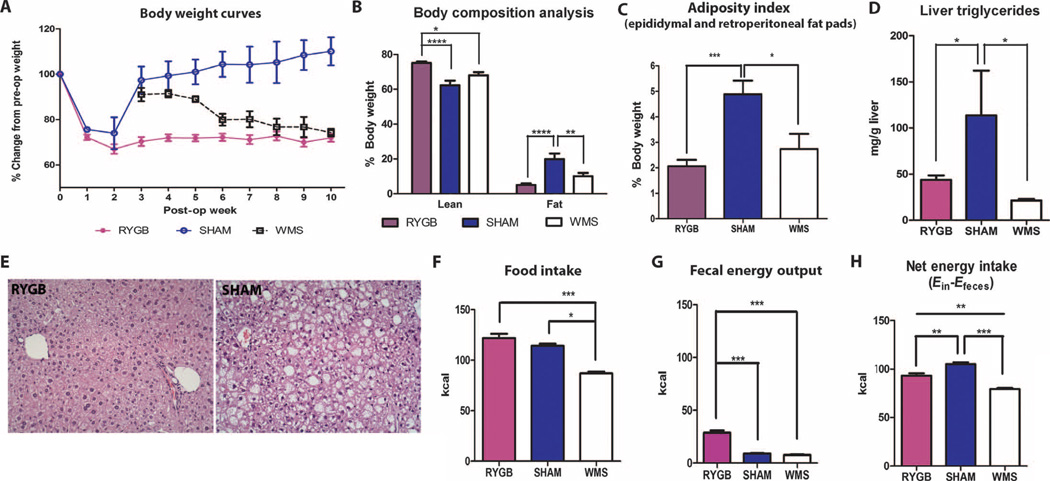
Fig. 2.
Phenotypic data from the RYGB mouse model. Characteristics of DIO C57BL/6J mice undergoing either RYGB (n = 11 to 17), sham operation (SHAM; n = 4 to 6), or sham operation with weight matching to the RYGB group by food restriction (WMS; n = 5 to 6). (A) Body weight curves after surgery. (B) Body composition analysis. (C) Adiposity index calculated from epididymal and retroperitoneal fat pad weights. (D) Liver triglyceride content. (E) Liver histology (×20). (F to H) One-week cumulative (F) food intake, (G) fecal energy output, and (H) net energy intake in RYGB (n = 14), SHAM (n = 11), and WMS (n = 6) animals. Measurements for (B) to (E) were taken at the end of study, 15 weeks after surgery. Food intake and energy output studies were performed 4 to 6 weeks after surgery. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and post hoc Tukey test. Values represent means ± SEM.